Seakeeper 40 Installation Manual (90715-2) 40-234-0043 to Current
Seakeeper 40 Installation Manual (90715-2) 40-234-0043 to Current
1.0 Introduction
Seakeeper 40
Installation Manual
90715, Revision 2

This document is intended to give details and guidance to a boat builder or equipment installer to install the Seakeeper 40 (40-241-0043 to Current).
Referenced Documents
1.1 Precautions
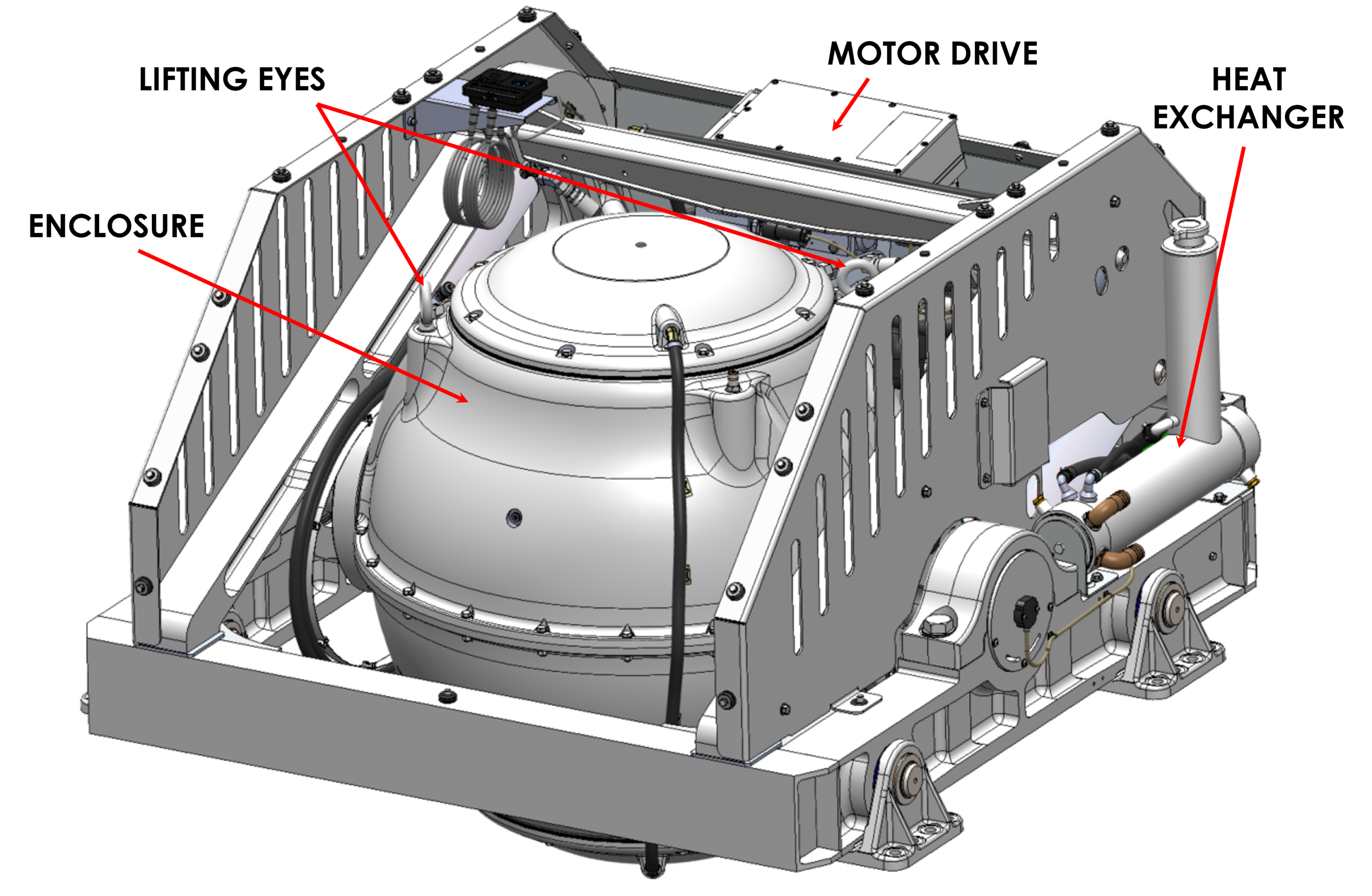
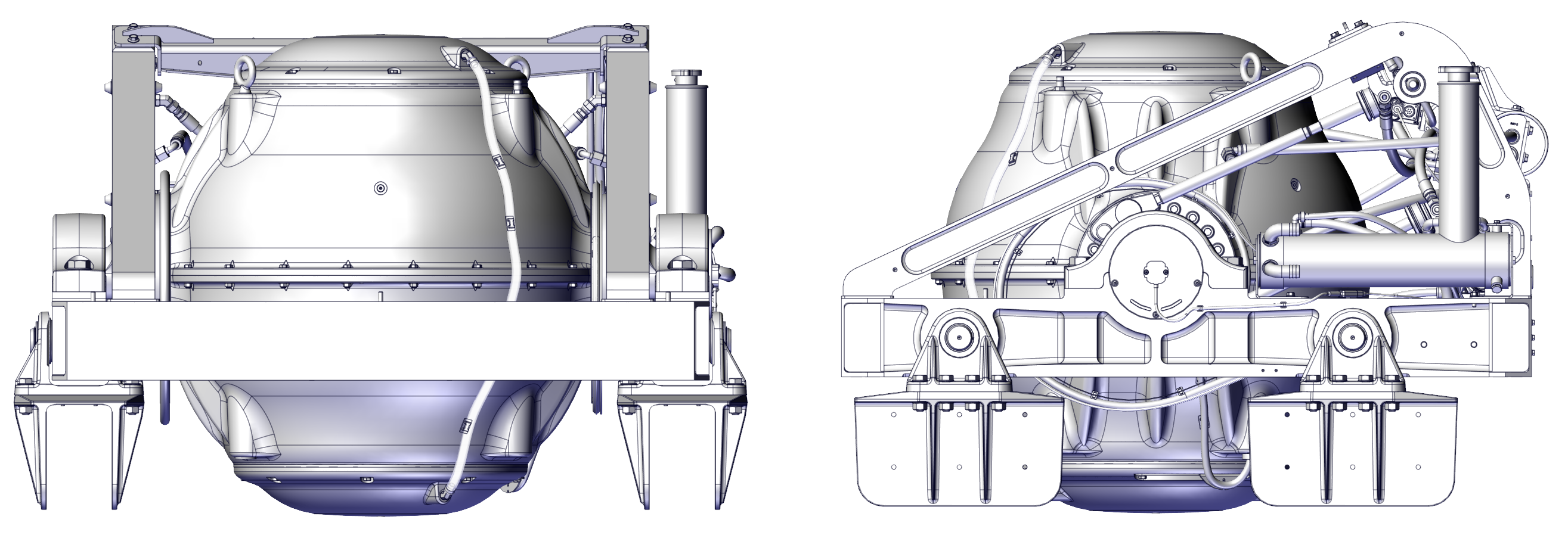
- The Seakeeper must only be lifted from the supplied lifting eyes shown in Figure 1 (see Section: Transport and Unpacking).
- The Seakeeper flywheel is supported by precision bearings. DO NOT drop or impart mechanical shock to the Seakeeper assembly when lifting or unpacking, as damage to bearings could result.
- While handling / installing the Seakeeper assembly, protect exposed hydraulic brake cylinder rods from scratches or damage as this could lead to premature seal failure and oil leaks.
- While handling / installing the Seakeeper assembly, do not allow electrical fittings that exit bottom of the Seakeeper enclosure to come in contact with any surface or object as this could damage the fittings and potentially affect the vacuum integrity of the enclosure.
- Exercise care to protect the painted finish as damage to finish could lead to early appearance degradation of the installed Seakeeper.
Safety
There is a large torque about the gimbal axis when the Seakeeper is precessing. Seakeeper cover panels are provided to prevent personnel or equipment from contacting the Seakeeper while it is in operation. These covers should not be stepped on or have anything placed on top. The covers should always be in place during operation. The cover side panels contain safety shields as shown below. Do not operate the Seakeeper without these safety shields in place.
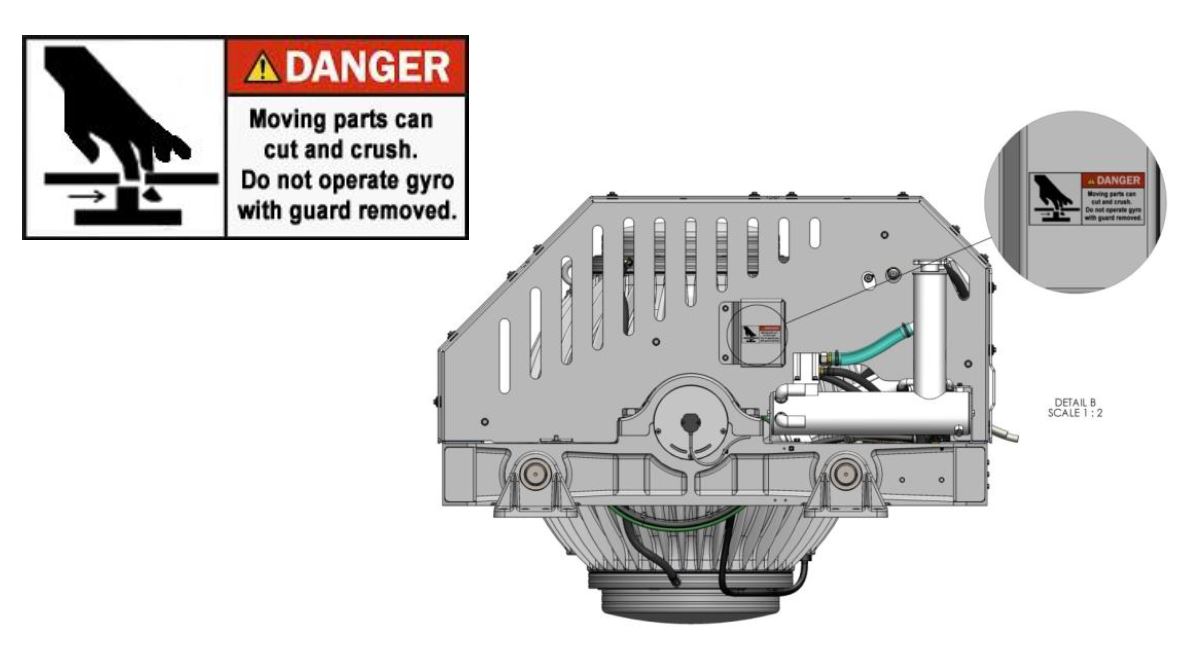
If it is ever necessary to access the Seakeeper while the flywheel is spinning, the Seakeeper must be locked at the display to stop the Seakeeper from precessing. Seakeeper regular scheduled maintenance should not be attempted unless the Seakeeper is locked and the flywheel has stopped spinning.
______________________________________________________________________________________________
If it is ever necessary to access the Seakeeper while the flywheel is spinning, the Seakeeper must be locked at the display to stop the Seakeeper from precessing.
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
Stand clear of the Seakeeper and all moving parts when operating.
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
The unit may be started remotely. Assume it could move without warning.
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
The Seakeeper and related structure should be treated with the same respect one gives a high-speed rotating propeller or engine shaft.
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
The following must be true before accessing the Seakeeper for service:
* Input power must be disconnected for at least 10 minutes
* The Seakeeper must be locked (Not in Sea Mode)
* Flywheel must be at zero speed
1.2 Transport & Unpacking
Reference Documents
Transport
- Use a Seakeeper provided shipping crate for transport. Overall dimensions of a fully packed crate are
58 L x 61 W x 53 H in. (1.32 L x 1.35 W x 1.19 H m) with a weight of 4,506 lbs (2,043 kg). - Do not stack Seakeeper shipping crates.
- Both Air and Ground transport are acceptable.
- Seakeeper shipping crates must be transported in environmental conditions between -4°F and 140°F (-20°C and 60°C).
Unpacking Crate
- Reference Seakeeper Drawing No. 12552– Seakeeper 40 Crated Gyro for items that ship with the corresponding Seakeeper model.
- Remove electrical components, cables, and misc. items and set aside.
- Remove packing materials that secure Seakeeper assembly inside the crate.
- Remove top and angled face cover panels to access lifting eyes. Store panels and hardware for reassembly.
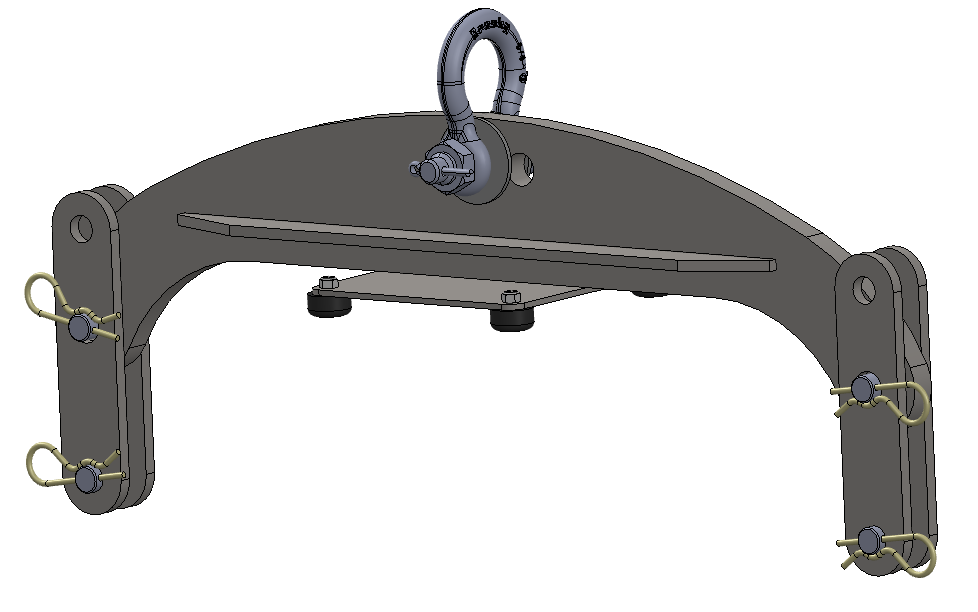
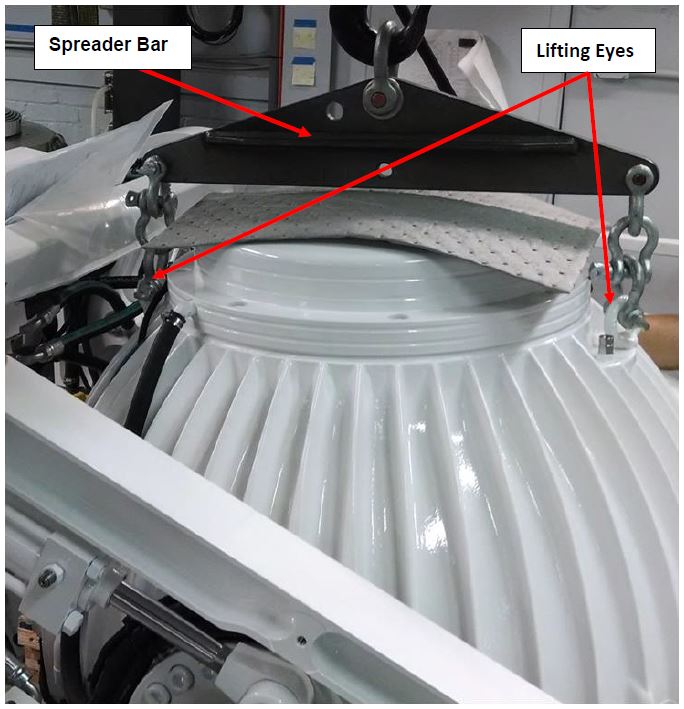
- Attach spreader bar (P/N 80029) to the two lifting eyes located on the top of the Seakeeper enclosure. Stay clear of any other parts on the Seakeeper. See image below.
- The Seakeeper 40 weighs 4,074 lbs (1,848 kg) with covers.

2.0 Mechanical Installation
2.1 Mechanical Installation Introduction
The Seakeeper can produce loads up to 11,381 lbs (50.6 kN) at each of the four mounts and careful consideration should be given to foundation design to ensure it can transfer these loads into the hull. These loads do NOT include vessel motion accelerations, such as vertical slam loads which can be significant for high speed vessels. The responsible party for designing the supporting structure (boat builder, installer, or hired sub-contractor) must accommodate the above forces plus a reasonable factor of safety. Seakeeper recommends a minimum safety factor of 3.0 (yielding a Safety Margin of 2.0).” The Seakeeper 40 FRB supports Bolt-In and Bond-In Installation methods.
It is assumed that the installer is familiar with mechanical fasteners to marine structures and has performed structural analysis to assure the structure to which the Seakeeper mounts, can properly transfer the loads the Seakeeper creates into the hull structure. If the installer has any doubt about the ability of the structure to transfer the loads to the hull, then a licensed naval architect or marine engineer should be contacted to do a structural analysis.
The installer should review the following list of reference drawings to ensure the installation procedure is fully understood.
Reference Documents & Drawings:
- 90713 – Seakeeper 40 Bolt-In Clearances
- 90714 – Seakeeper 40 Bolt-In Installation Details
- 90878 – Seakeeper 40 Bond-In Installation Details
- 90088 – Bond-In Installation Fixture Kit
- 90089 – Seakeeper 40 Bolt-In Installation Fixture Kit
- 90614 – Seakeeper 40 Bolt In Kit (Optional)
- 90086 – Seakeeper 40 Thru-Bolt Kit (Standard)
- 90287 – Seakeeper Bond-In Saddle Kit
- TB-90382 – Structural Adhesive Recommendation
2.2 Selection of Installation Location
Selection of mounting location of the Seakeeper should consider the following desirable features:

The Seakeeper should be installed aft of amidships to minimize high acceleration loadings due to hull/wave impacts during operation at high speed or in large waves. If the only possible installation location is forward of amidships, then the installer should have Seakeeper review the installation location prior to finalizing the design.
Seakeeper can only assess installation location regarding its impact on Seakeeper operation and serviceability. Seakeeper cannot determine how the installation location will affect the vessel static or directional stability other than cyclic roll reduction. The Installer is responsible for considering the Seakeeper’s effect on the CG location, trim, overall stability, and performance of the vessel.
The Installer is solely responsible for ensuring that the Seakeeper is properly located and installed on the vessel foundation with an adequate margin of safety for the specified design loads and vessel operating characteristics.
Selection of mounting of the Seakeeper should consider the following desirable features:
- Overhead access or sufficient clearance for removal / re-installation of the Seakeeper for overhaul in future years per Figure 3.
- The Seakeeper should be installed in a dry space to minimize effects of corrosion.
- Clearance for replacement of gimbal angle sensor on gimbal shaft (see Figure 3).
- Clearance for filling / purging brake hydraulic oil (see Figure 3).
- Clearance for filling water/glycol cooling circuit (see Figure 3).
- Clearance for replacement of brake hydraulic cylinders (see Figure 3).
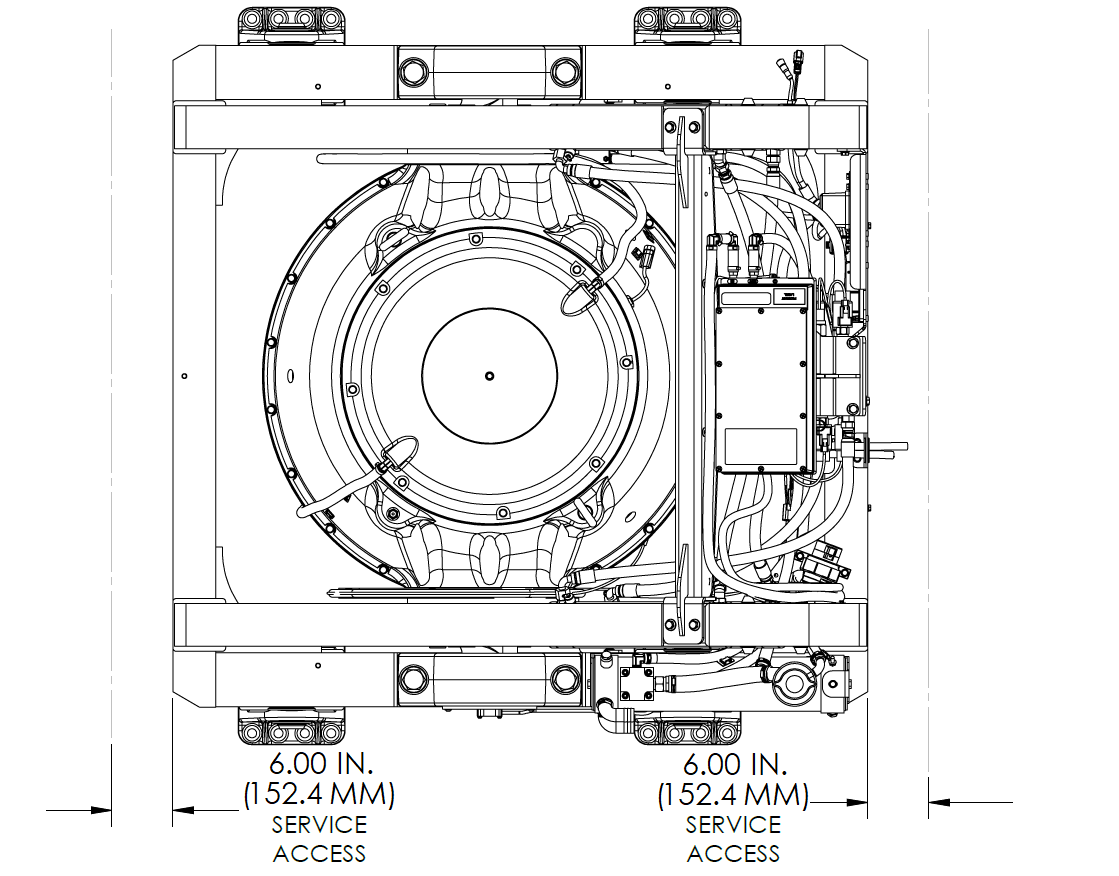
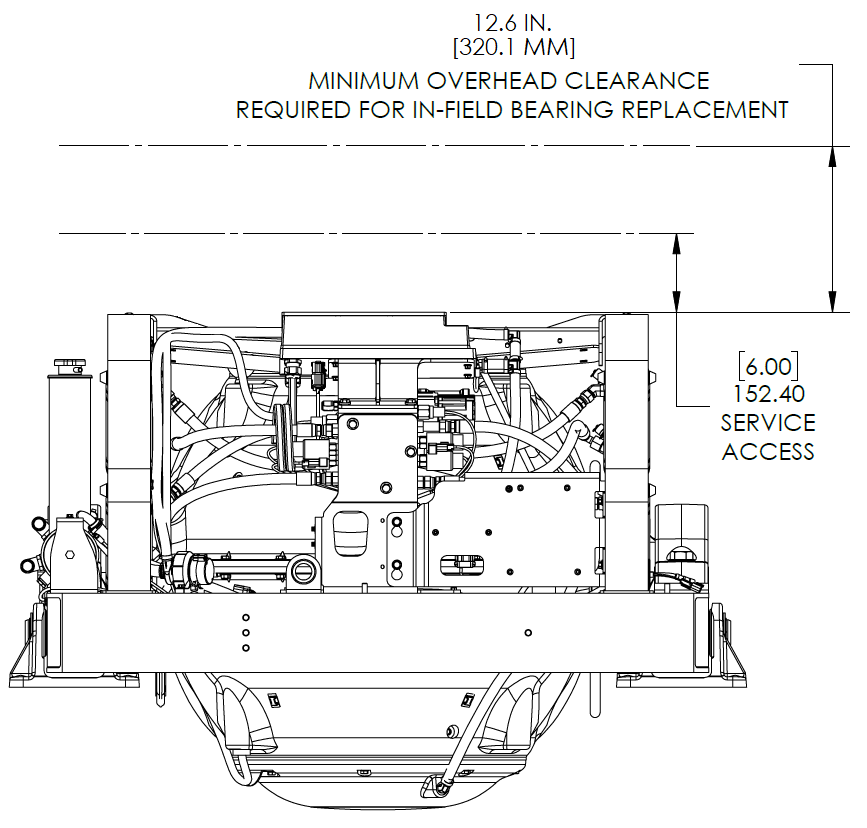
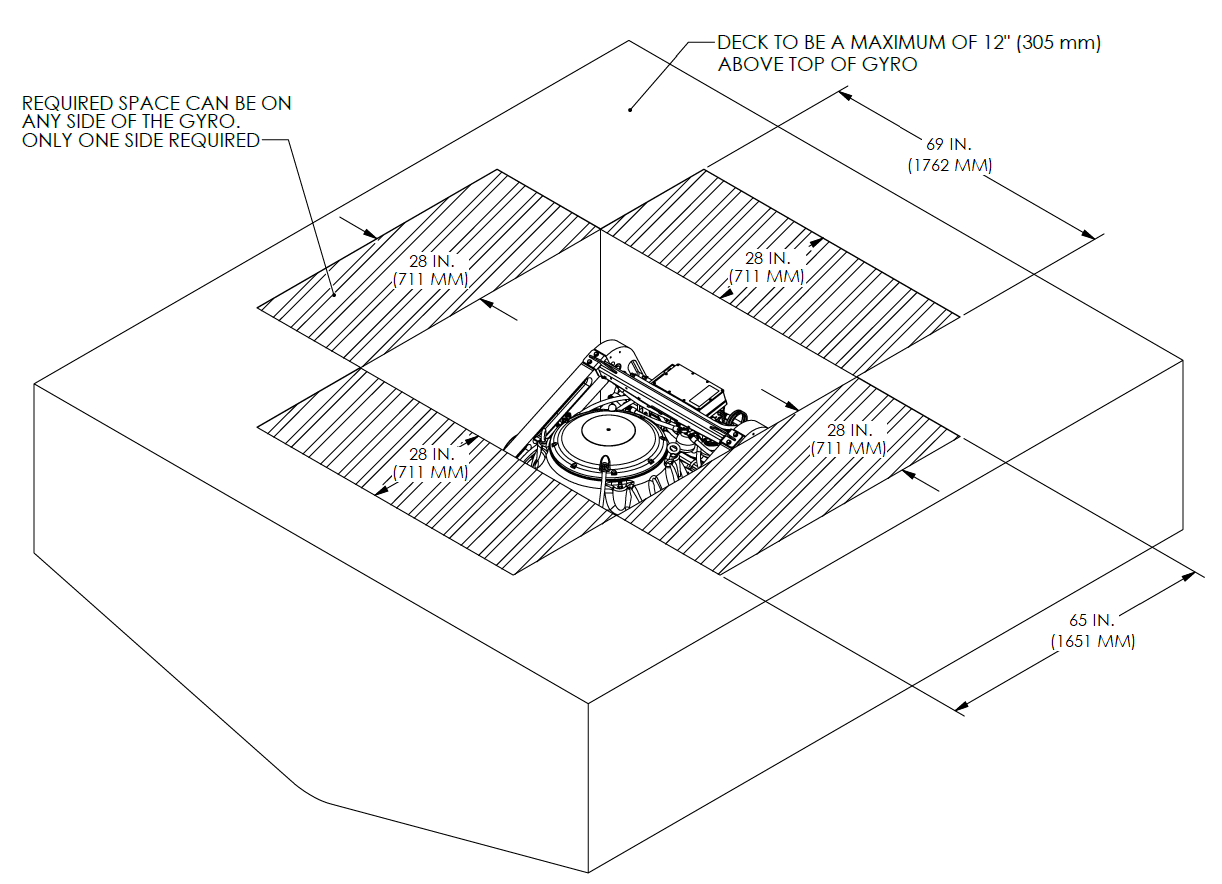
VIEWS SHOWING RECOMMENDED CLEARANCES AROUND THE SEAKEEPER FOR USE OF HANDTOOLS, EASE OF MAINTENANCE, INSTALLATION, AND PROPER OPERATION.
Figure 3 – Seakeeper 40 Installed Clearance Considerations
6 in. (152 mm) on each side with one side having 28 in. (711 mm)
12.6 in. (320 mm) overhead service clearance
2.2.1 Noise/Soundproofing
Seakeeper noise has been measured under steady state conditions (no wave load) in Seakeeper‘s Engineering Lab. The steady state noise is typically < 73 dBC at 1 meter. As the frequencies emitting the highest sound pressures are low (like other marine machinery), it is recommended that the Seakeeper be installed in a machinery space that is already treated with soundproofing.
2.3 Selection of Installation Method
The Seakeeper 40 FRB can be affixed to the hull structure using two methods 1) Bolt-In installation or 2) Bond-In (Saddle) installation. See figures below.
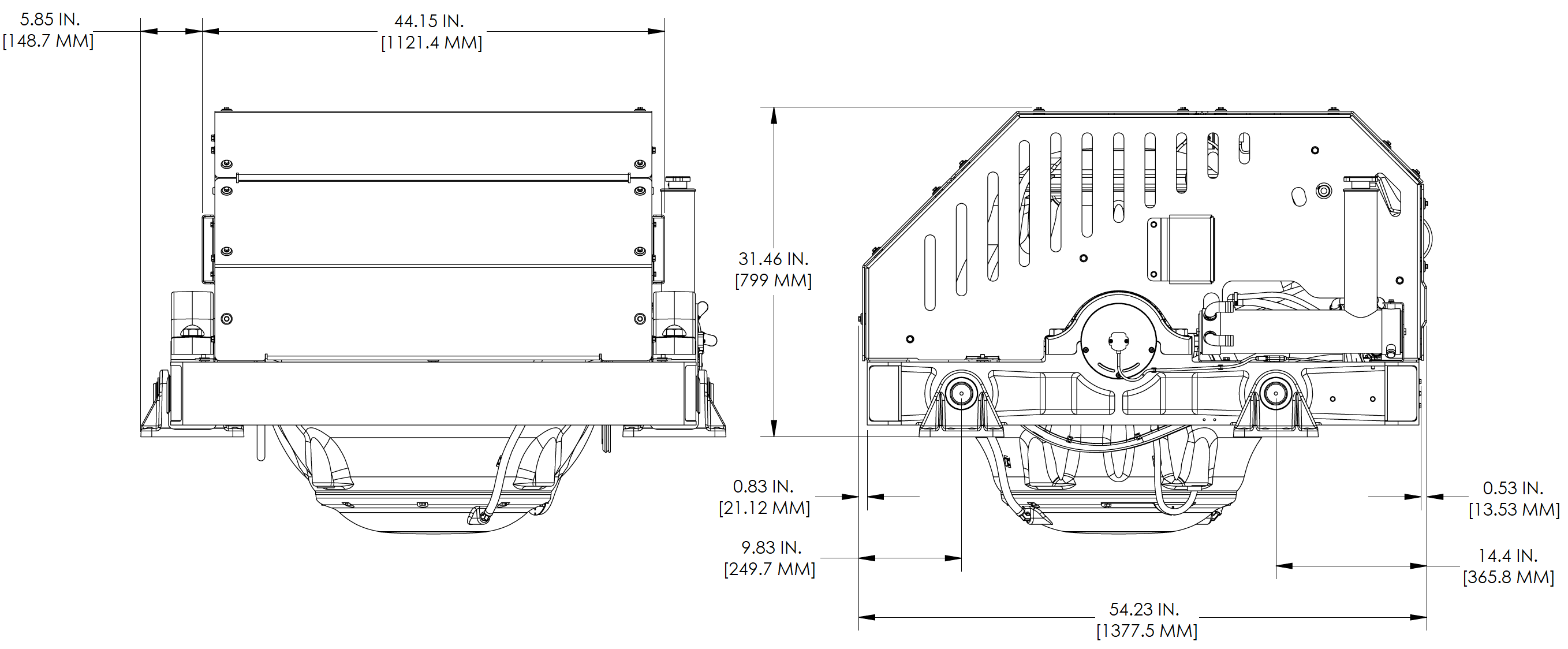
Option 1 would be applied when a metal structure or laminated metal plates are available for attachment. The foundation would fasten directly to the hull structure or plates using isolation gaskets for metal-to-metal contact using 32 x M16-1.0 fasteners. Depending on the structure to which the Seakeeper is fastened, blind threaded holes (Seakeeper Part No. 90614) or thru-bolting (Seakeeper Part No. 90086) can be utilized.
Option 2 would be commonly used on a hull constructed of glass-reinforced plastic (GRP) or fiberglass. For this option, four 16.0 in. (406 mm) long by 8.0 in. (203 mm) deep saddles (Seakeeper Part No. 90287) are bonded to properly spaced and prepared structural members that are an integral part of the hull structure. Seakeeper recommends using a structural adhesive with a lap shear strength of 2000 psi (13.8 MPa) or greater, such as Plexus MA590. Careful consideration should be exercised by the installer while selecting the appropriate adhesive. Compatibility with the Seakeeper’s cast aluminum A356-T6 saddles, hull structure, and pot life are three critical factors. Proper surface preparation per the adhesive manufacturer’s recommendations before installation is required.
Note: If bonding saddles to a metal structure, contact Seakeeper for hull preparation instructions.
2.4 Bolt-In Installation
2.4.1 Preparation of Vessel Structure
Seakeeper provided mounting hardware is intended to apply to typical installation arrangements. However, each installation, especially custom aftermarket foundations, should be thoroughly reviewed to ensure the provided hardware meets the required thread engagement for the Seakeeper unit being installed. The mounting bolt thread engagement requirements are outlined in the Installation Manuals and Installation Details Drawings for each Seakeeper model. This also applies to Seakeeper model adapter kits and OEM built frames where the bolt hole depth should be checked to ensure the bolts will not bottom, preventing the bolts from achieving the intended preload.
When the Seakeeper provided hardware is not appropriate, the bolt specification (diameter and thread pitch) and grade should be matched in the required length and used with the Seakeeper provided washers. Mounting bolts should always be torqued to the Seakeeper specification. All Seakeeper provided bolts are metric course thread. Hardware specifications are also listed in the Installation Manuals and Installation Details Drawings.
Refer to Seakeeper Drawing No. 90714 – Seakeeper 40 Bolt-In Installation Details. Important dimensional and load information is given in this drawing that will impact the design details of the structure that will receive the Seakeeper. It is assumed that a proper structural analysis has been performed for the hull structure to which the Seakeeper will be fastened to ensure proper strength margins for the loads the Seakeeper will create during operation.
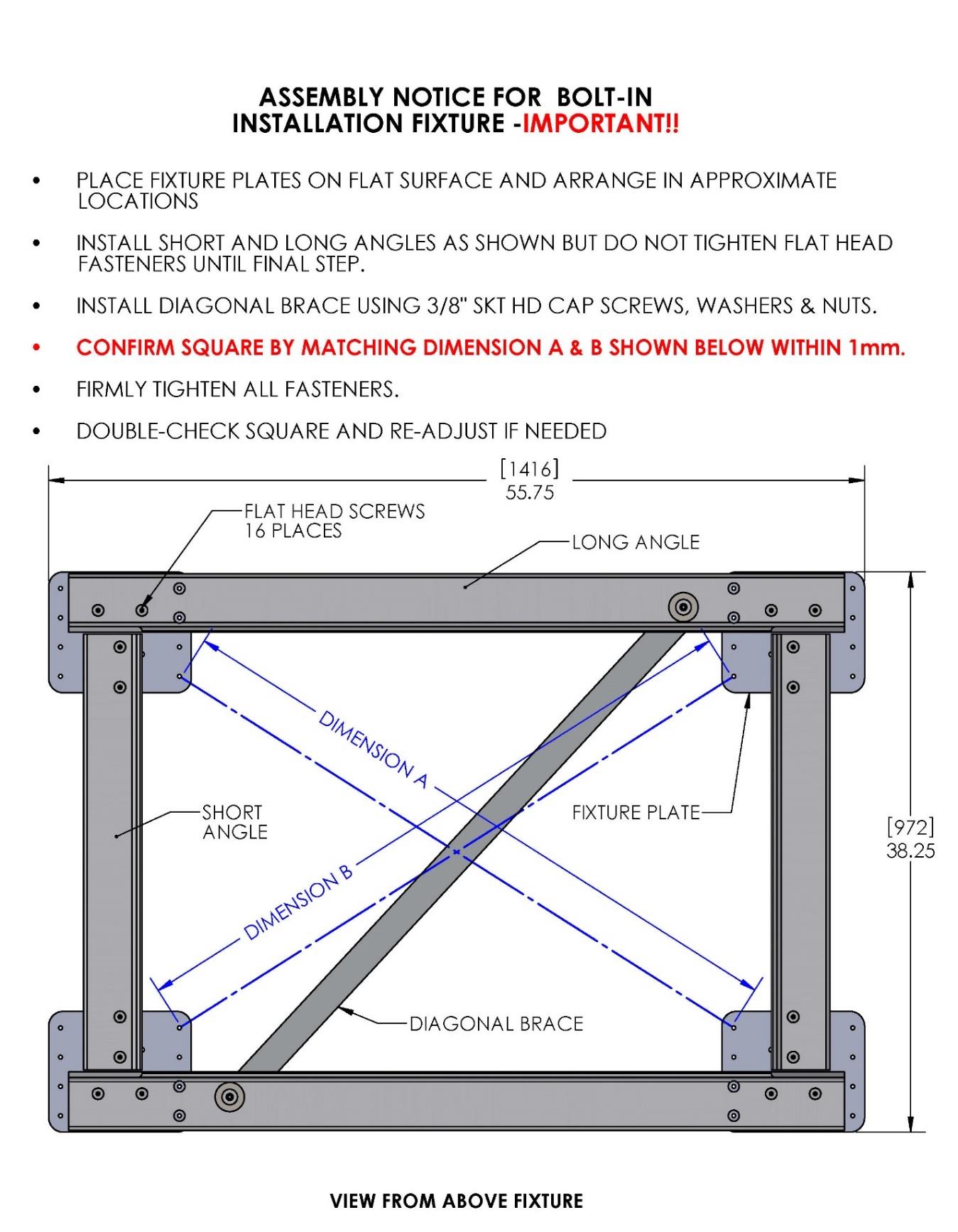
The hull structure supporting the Seakeeper should be arranged so the Seakeeper is parallel to the waterline in the forward-aft and port-starboard directions (with up to 2° allowance for trim). In addition, the four areas on top of the beams on which the isolation mounts will rest, need to be co-planar within 0.13 in. (3 mm) to minimize potential distortion of Seakeeper support frame when installed.
Seakeeper provides an installation fixture assembly (P/N 90089), which contains four plates that mimic the mating surfaces of the four isolation mounts located on the Seakeeper’s foundation. These plates have 8 holes located at the same centers as the holes in the isolation mounts. These smaller holes can be used to locate the holes in the ship’s structure through use of a transfer punch or drill. The fixture locates the hole patterns at the proper spacing, both in the fore-aft direction and the port-starboard direction. See Figures 4 & 5 below. Once assembled, the fixture can be used to check clearances and alignment of the hull structure.
Note: Do NOT use the installation fixture to establish Seakeeper envelope dimensions. Refer to Drawing No. 90714 – Seakeeper 40 Bolt-In Installation Details, for envelope dimensions. A 3-D model of the Seakeeper is available on the Seakeeper website (www.seakeeper.com) to aid in designing the Seakeeper foundation and the space around the Seakeeper.
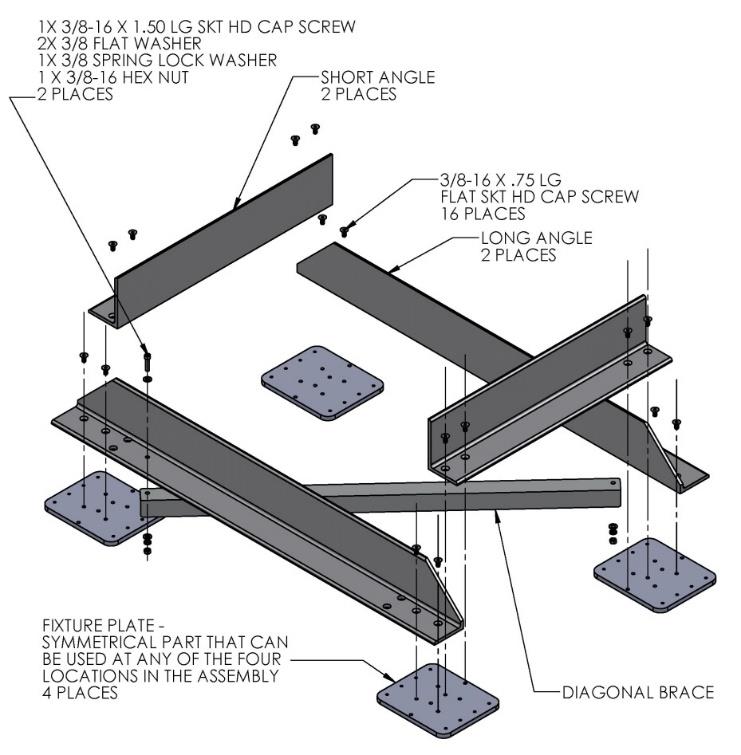
CAUTION: Tight clearances from cable guide bands to hull structure. See above figure for dimensions and reference Seakeeper Drawing No. 90714 – Seakeeper 40 Bolt-In Installation Details, for complete envelope.
2.4.2 Transfer of Holes to Boat Structure
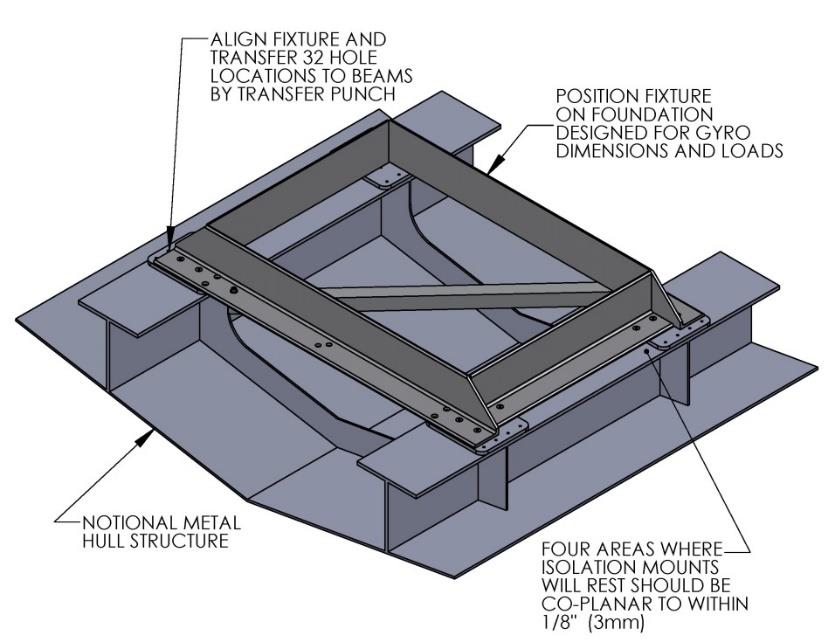
- Lower assembled fixture onto hull structure.
- The four areas where the isolation mounts will rest should be coplanar to within 0.13 in. (3 mm). See figure below. Do not use the fixture to check co-planarity as it is not stiff enough.
- Align fixture in desired location and transfer holes from fixture plate to the hull structure. A transfer punch is recommended for this step. Note that holes in fixture plate are 0.257 in. (6.5 mm) in diameter.
- Remove fixture and drill holes in hull structure at marked locations to mate with holes in Seakeeper isolation mounts. A 0.689 in. (17.5 mm) diameter hole is recommended for the provided M16 fasteners.
NOTE: Certain foundation designs that employ threaded blind holes in thick plates may require the installer to obtain alternate fasteners.
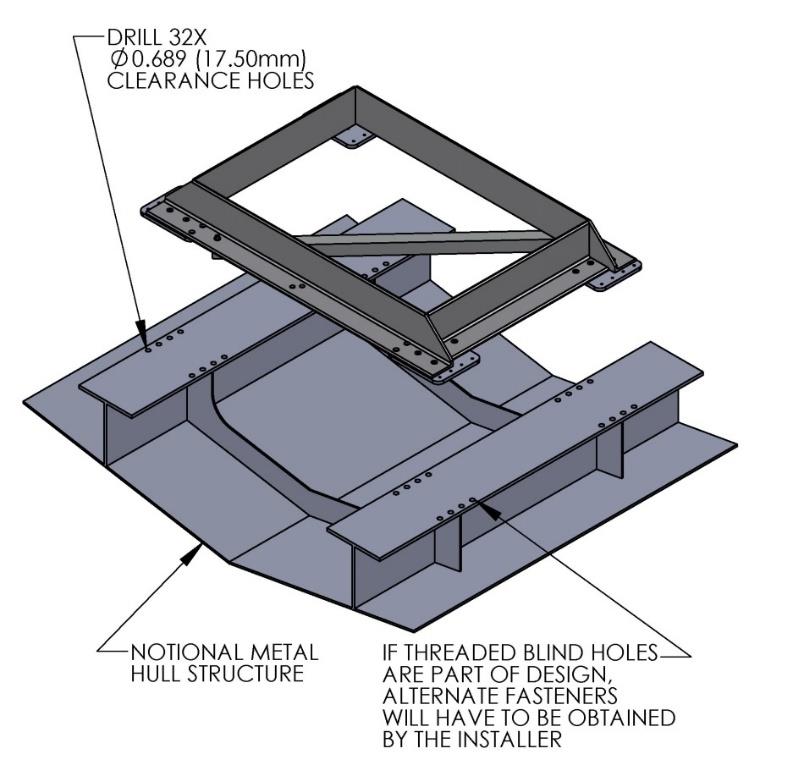
2.4.3 Installation of Seakeeper
- Locate and position 4 isolation gaskets (P/N 10534) onto foundation beams (for metal to metal contacts only).
NOTE: A FILM OF SEALANT SHOULD BE APPLIED TO THE GASKET TO KEEP WATER FROM WICKING INTO THE JOINT. - Lower Seakeeper into position onto foundation beams and align over drilled holes.
- Install Mounting Bolts:
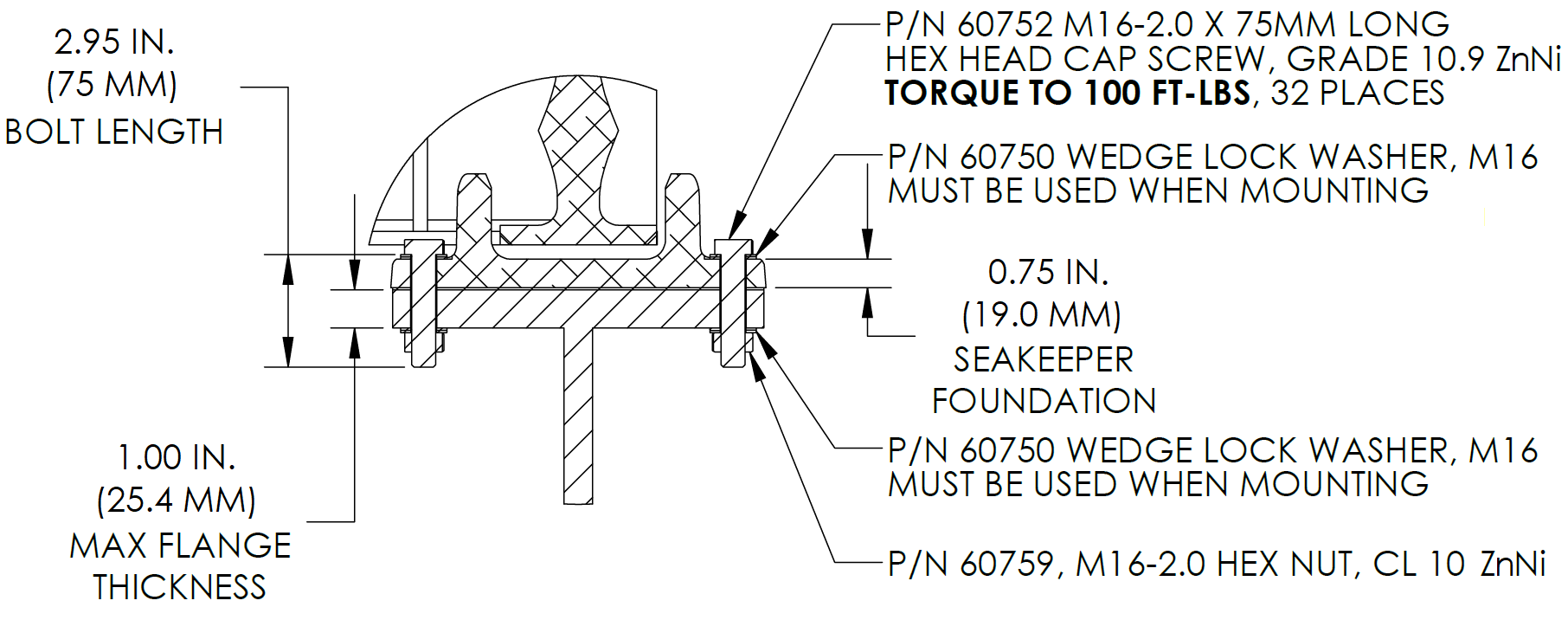
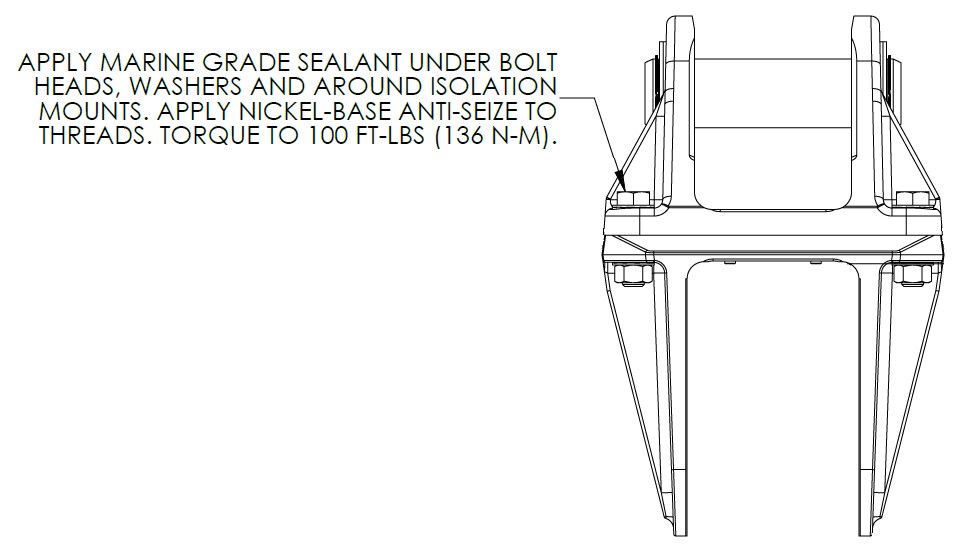
- For Through-Bolt installations (P/N 90086 – Seakeeper 40 Thru-Bolt Kit), install the Seakeeper supplied M16-2.0 fasteners to maintain a minimum of 2 threads protruding past nut. Apply a moderate coat of nickel-based anti-seize (e.g., SAF-T-EZE nickel grade anti-seize, SBT-4N or equivalent) to the threads of each bolt and include a small bead of marine grade sealant (e.g., SILI-THANE 803 or equivalent) under each bolt head and washer before installation. See Figure 6.
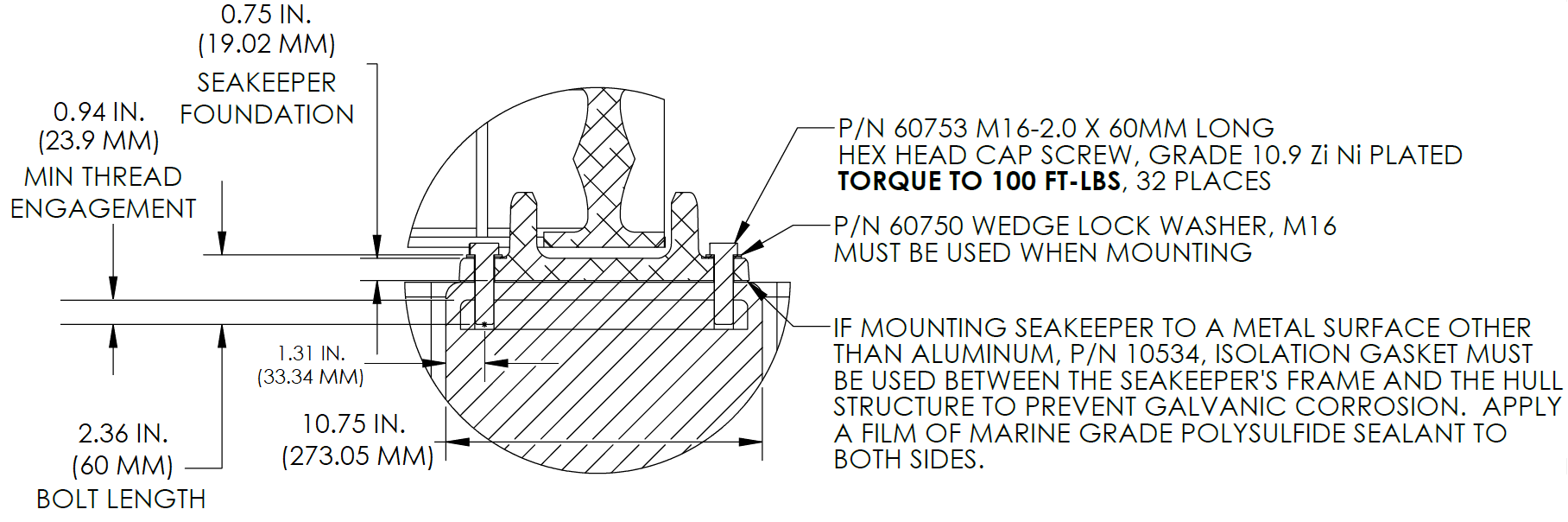
- For Blind-Hole installations (P/N 90614 – Seakeeper 40 Bolt-In Kit), install the Seakeeper supplied M16-2.0 fasteners to maintain a minimum thread engagement of 0.95 in. (24 mm). Apply a moderate coat of nickel-based anti-seize (e.g., SAF-T-EZE nickel grade anti-seize, SBT-4N or equivalent) to the threads of each bolt and include a small bead of marine grade sealant (e.g., SILI-THANE 803 or equivalent) under each bolt head and washer before installation. See Figure 7.
- Torque all fasteners to 100 ft-lbs (136 N-m).
- New bolts, matching the Seakeeper specification, must be used for each installation and reinstallation that meet the requirements listed above.
- Proceed to electrical and cooling portion of the installation.
2.5 Bond-In Installation
2.5.1 Preparation of Vessel Structure
Refer to Seakeeper Drawing No. 90878 – Seakeeper 40 Bond-In Installation Details. Important dimensional and load information is given in this drawing that will impact the design details of the structure that will receive the Seakeeper as well as selection of the adhesive to bond the Seakeeper into the hull. Reference TB-90382 – Structural Adhesive Recommendation for the recommended adhesives for bond-in installation.
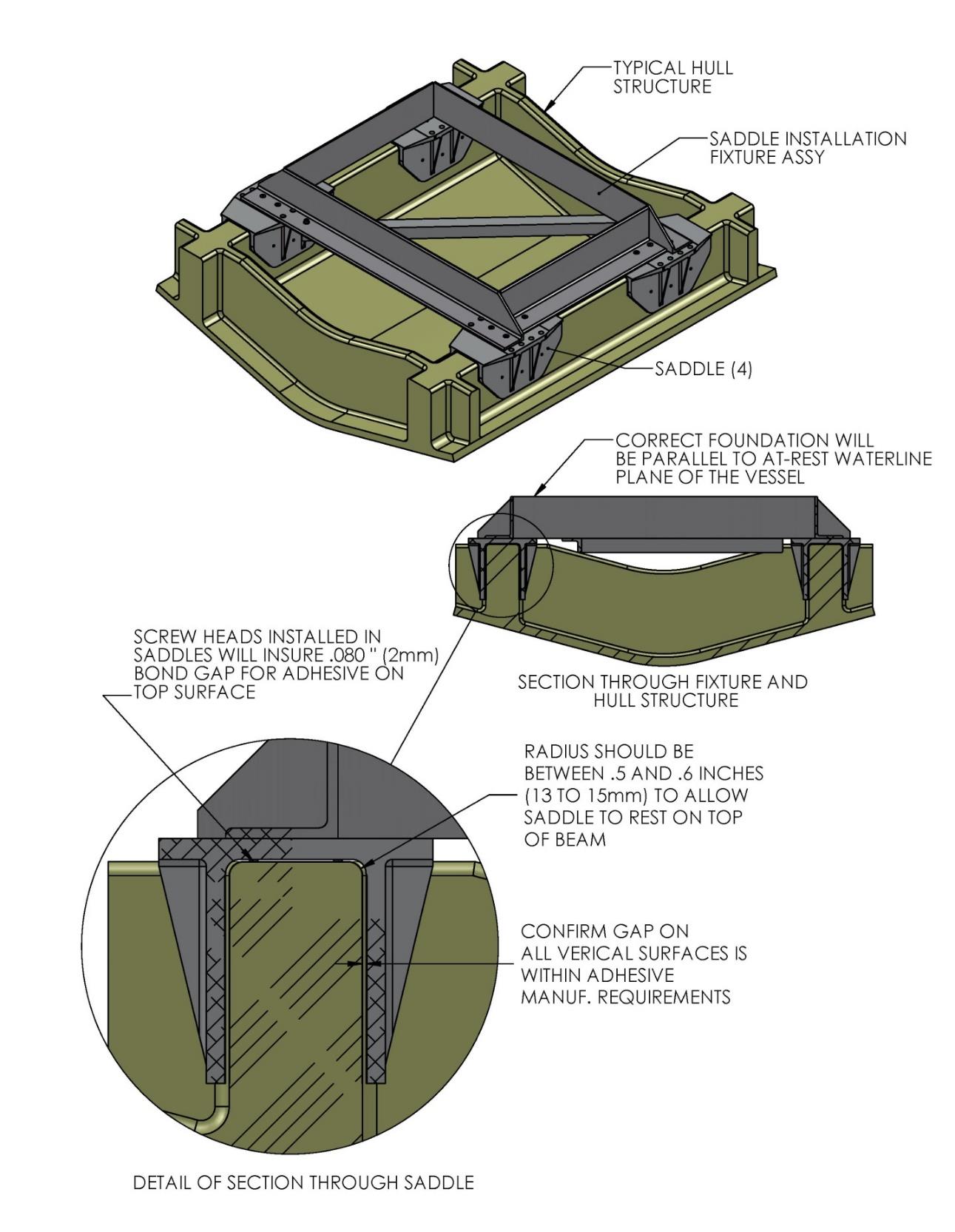
The foundation “saddles” of the Seakeeper are designed to be bonded directly to the composite hull structure of the vessel to effectively distribute Seakeeper loads. A complete bond is required between the inside surface of the saddles and the hull structure. An estimate of adhesive volume required should be calculated for each installation based on gaps between saddles and structural members. There is some adhesive waste as a part of the process so a good rule of thumb is to purchase 50% more adhesive than estimated volume to ensure a complete bond. Depending on conditions and adhesive used, two workers may be required to apply the adhesive at the same time to finish the installation before the adhesive starts to cure. To aid in determining the quantity of adhesive required, the interior surface area (bonding surfaces) of each saddle is 325 in.2 (2,097 cm2) for a total bonded surface area for all four saddles of 1,300 in.2 (8,387 cm2).
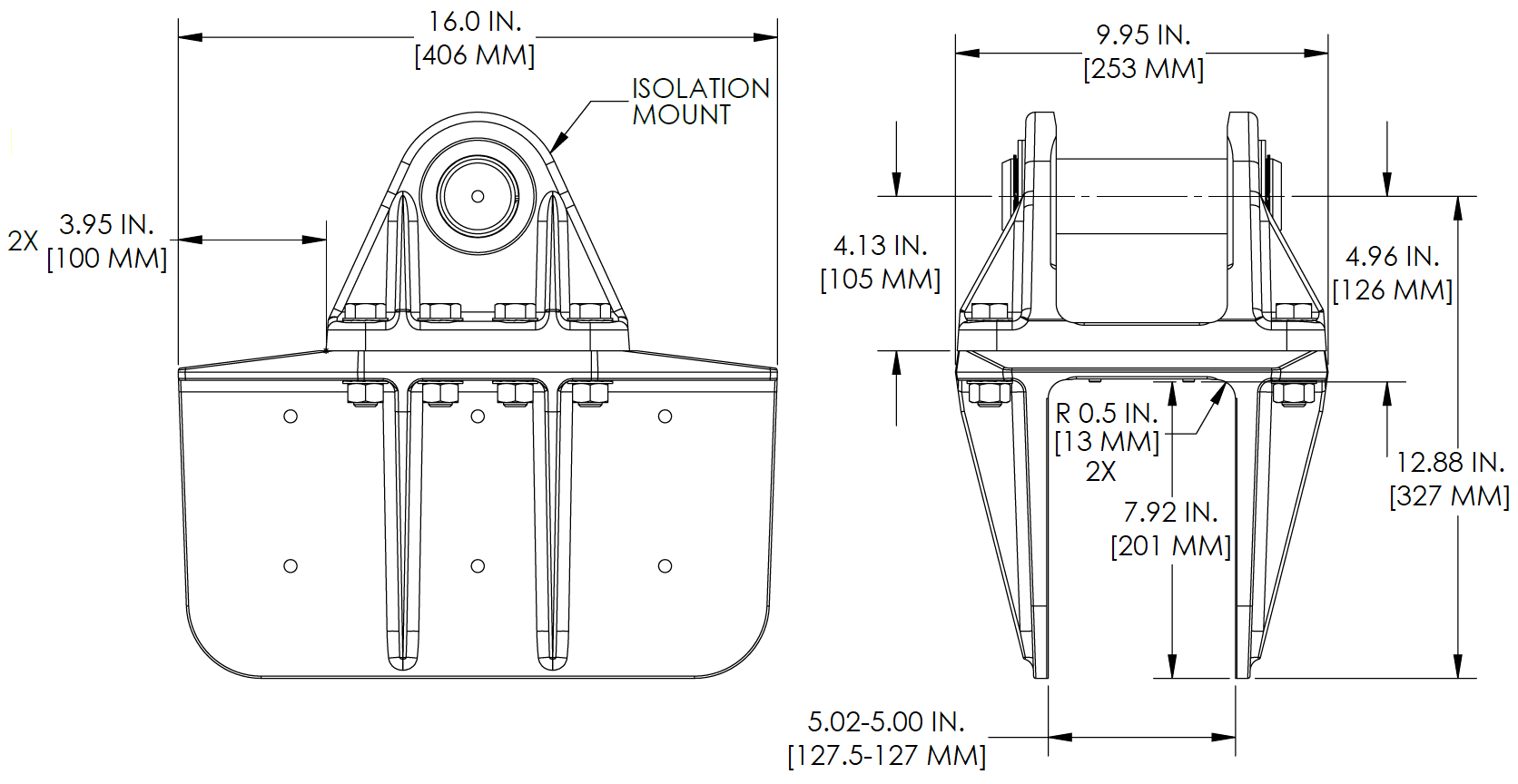
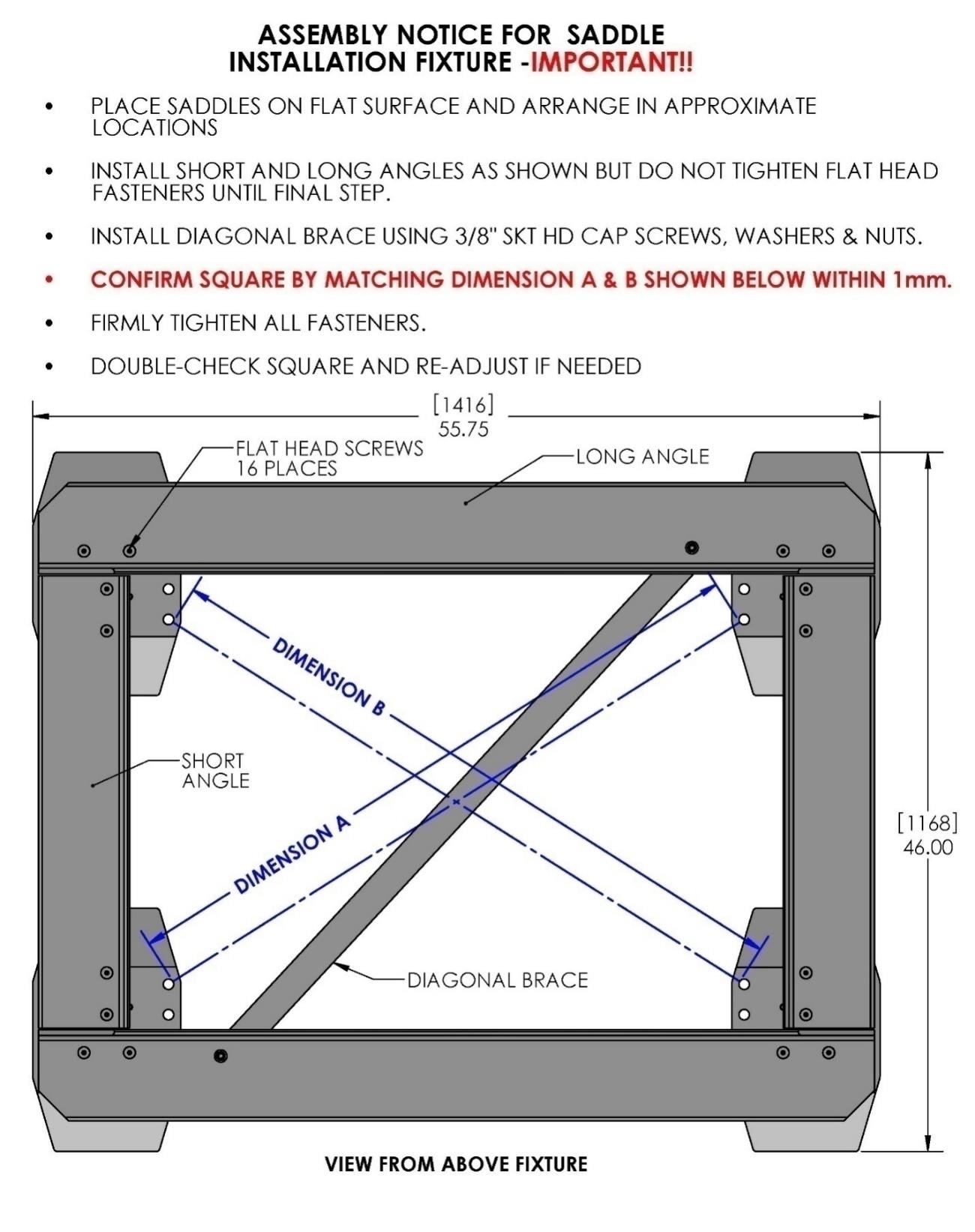
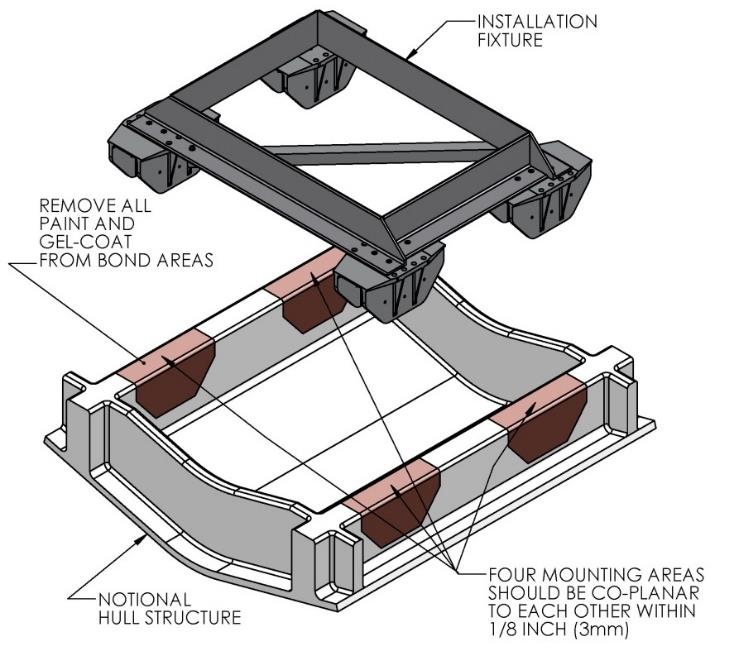
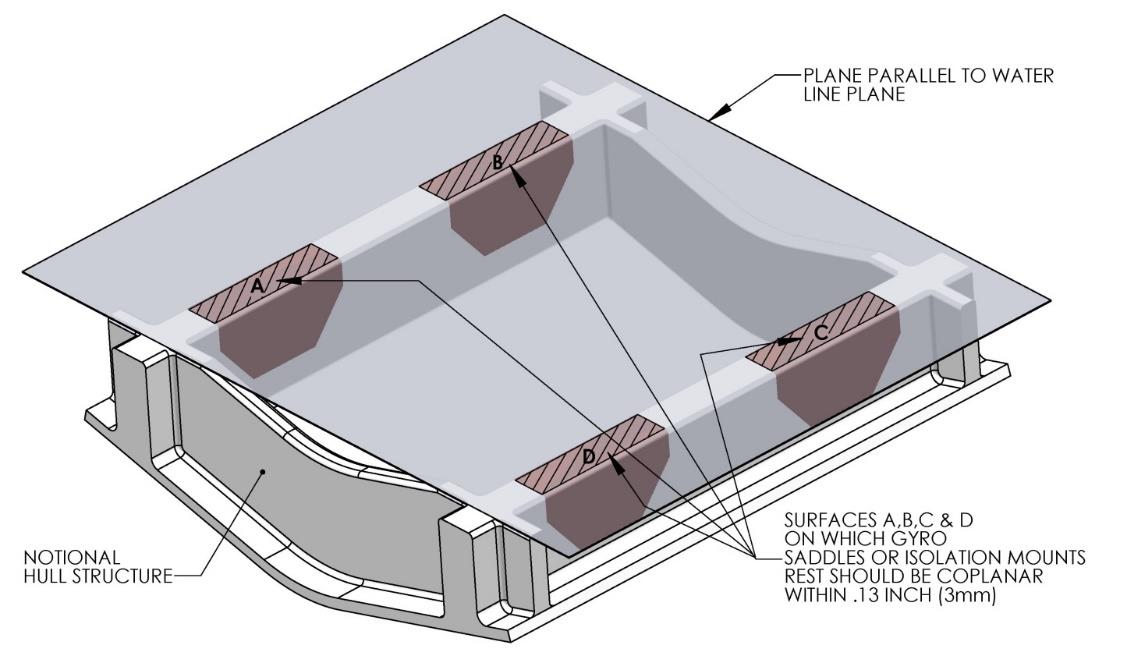
The hull structure supporting the Seakeeper should be arranged so the Seakeeper is parallel to the waterline. In addition, the four areas on top of the beams that the saddles will bond to need to be co-planar within 0.13 in. (3 mm) to minimize potential distortion of Seakeeper support frame when installed, as shown in Figure 13.
Note that any paint or gel-coat present in bond area should be removed so that adhesive will bond directly to laminate fibers and resin.
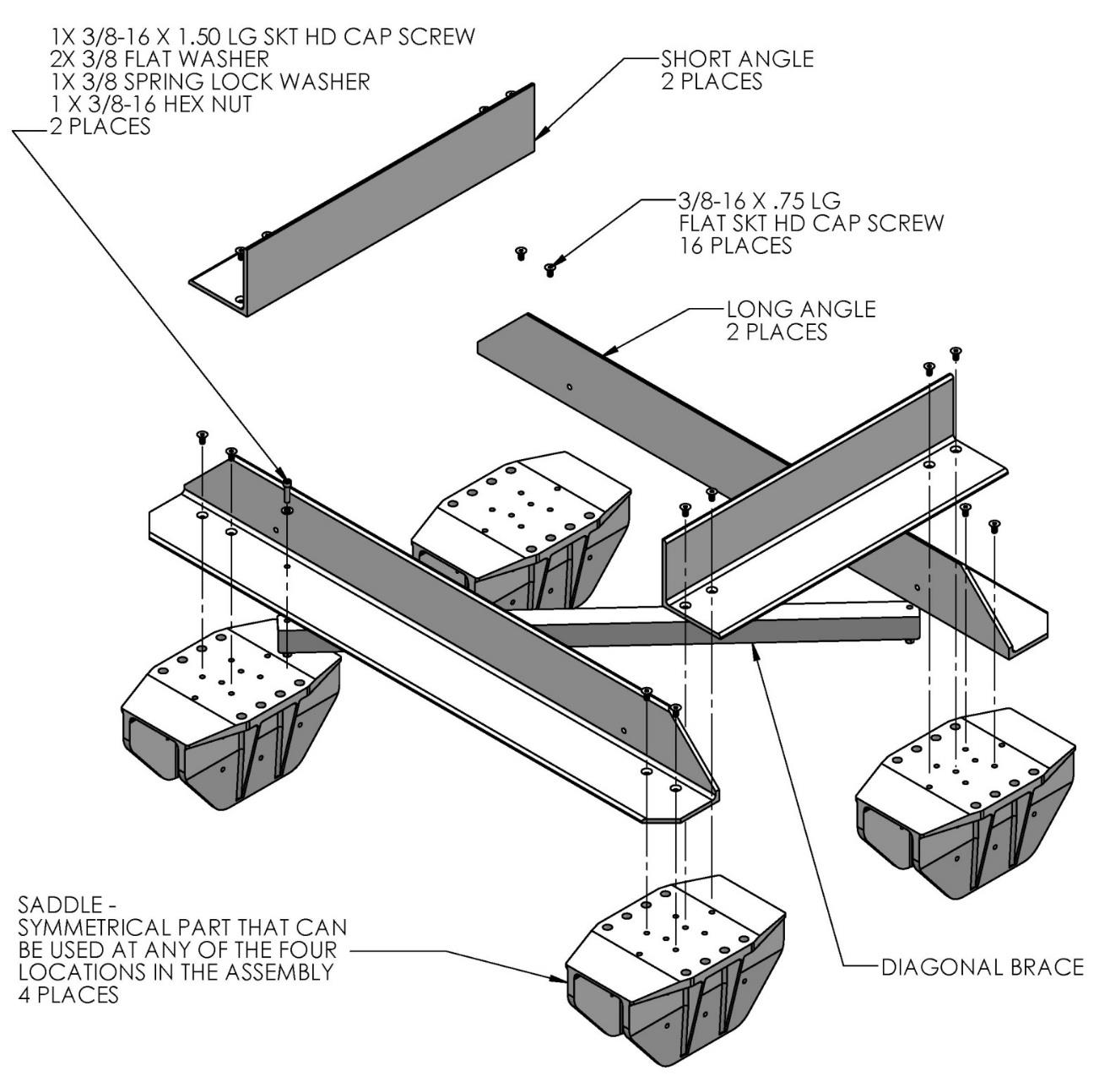
Seakeeper provides an installation fixture template (P/N 90088), that locates the saddles at the proper spacing both in the forward-aft direction and the port-starboard direction. See Figures 8, 9, and 10 below. Once assembled with the provided saddle fittings, the fixture can be used to check clearances and alignment of the hull structure. The fixture will allow the builder / installer to lay-up and adjust the foundation dimensions to create a low-clearance fit between the Seakeeper foundation saddles and the hull structure. Shear strength of the adhesive will be maximized if the cured thickness between the vessel structure and the Seakeeper saddles is at the thinner end of the adhesive manufacturer’s recommended range. Therefore, the fixture should be used to confirm that the overall dimensions of the foundations are square and level and that the adhesive gap is within Seakeeper’s recommended range of 0.04 in. to 0.13 in. (1 to 3 mm).
Note: Do NOT use the installation fixture to establish Seakeeper envelope dimensions. Refer to Drawing No. 90878 – Seakeeper 40 Bond-In Installation Details, for envelope dimensions. A 3-D model of the Seakeeper is available on the Seakeeper website (www.seakeeper.com) to aid in designing the Seakeeper foundation and the space around the Seakeeper.
Hull Preparation
- Position installation fixture (Figure 11) on hull girders noting recommended clearances for maintenance from Drawing No. 90878 – Seakeeper 40 Bond-In Installation Details. Check that the screws fastening the saddles to the installation fixture are tight (Figure 9).
- Mask hull area (as shown in blue, Figure 12) around foundation saddles for easy clean-up and to create an outline of surface area to receive adhesive, as shown in brown (Figure 13). Ensure that the bond gap is within adhesive manufacturer’s recommended thickness, or 3 mm if using Plexus MA590.
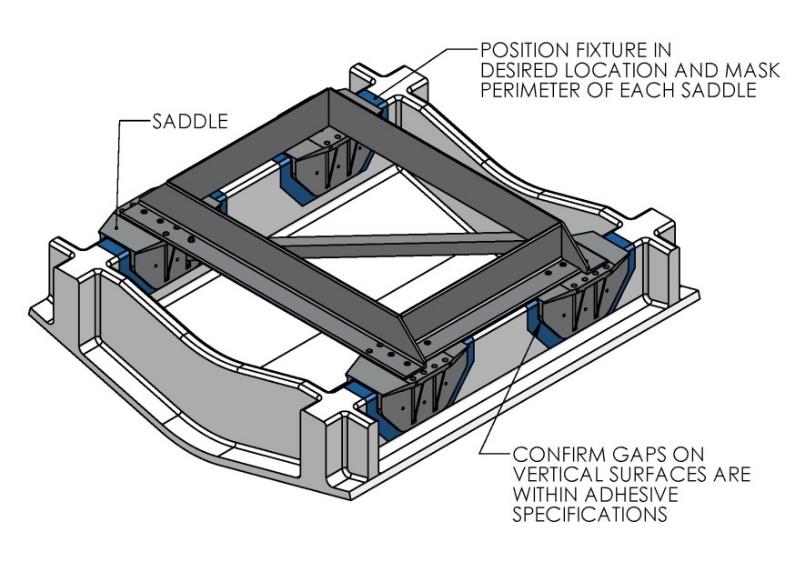
- Raise fixture clear of foundation. Check all four mounting areas are co-planar to within 0.13 in. (3 mm) to each other, as well as parallel to the water line plane, as shown in Figure 13.
- Thoroughly clean with alcohol or acetone all areas (highlighted in brown, Figure 13) of girders to be bonded to remove any contaminates. Use new paper towels for cleaning, not shop rags.
- Remove any paint or gel-coat from bond surfaces so that adhesive will bond directly to laminate fibers and resin.
- Thoroughly sand girder bond surfaces with 80 grit sandpaper. (IMPORTANT – BOND STRENGTH MAY BE REDUCED IF THIS STEP IS SKIPPED.)
- Wipe surfaces clean from dust with alcohol or acetone using new paper towels, not shop rags.
- Re-position installation fixture on girders and double-check that the adhesive gap is within the adhesive manufacturer’s maximum recommended thickness. Seakeeper recommends a maximum gap of 3 mm if using Plexus MA590.
- Lift installation fixture clear of foundation. Apply Seakeeper provided adhesive backed foam strips at the eight locations shown (each end of four saddles) in Figure 14 below. These strips are to serve as a dam to minimize adhesive escaping out the ends of the saddles as they are positioned over the bond area.
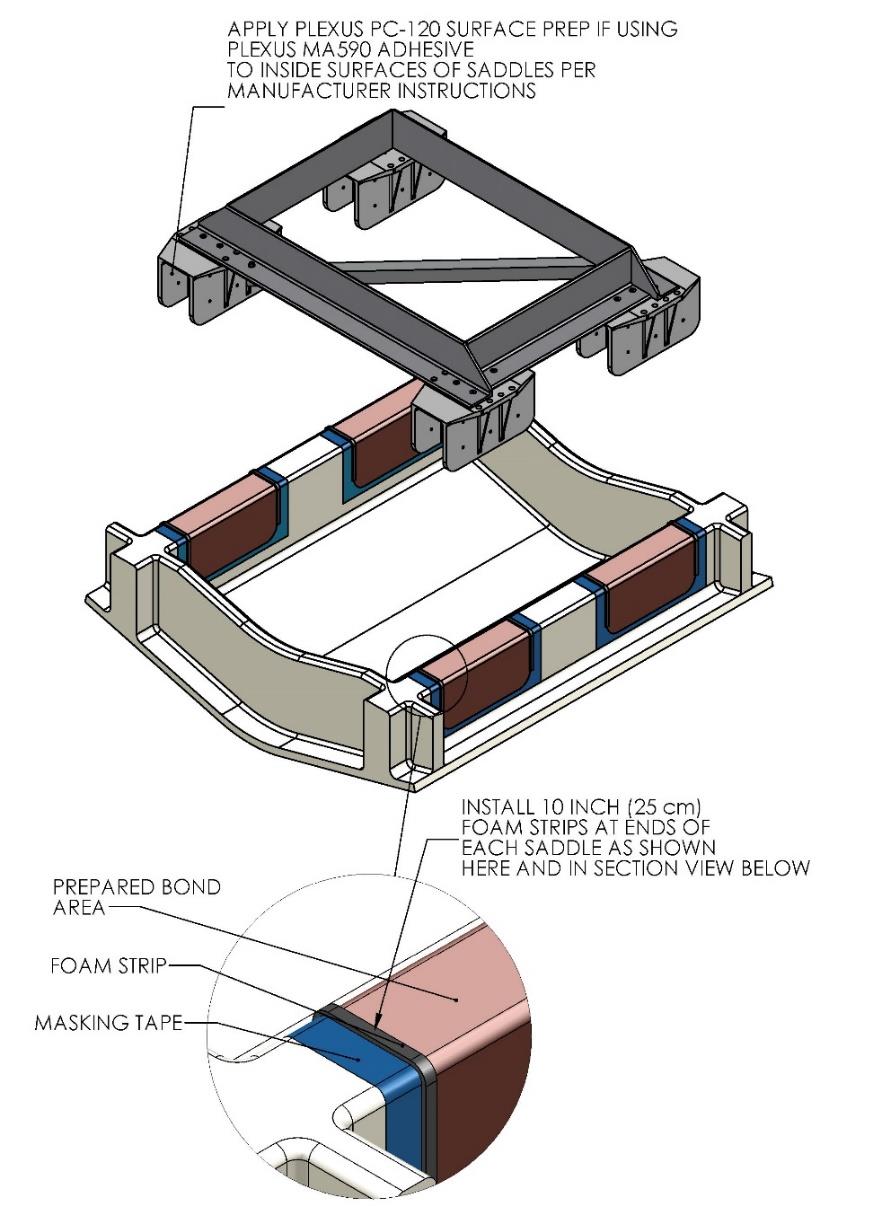
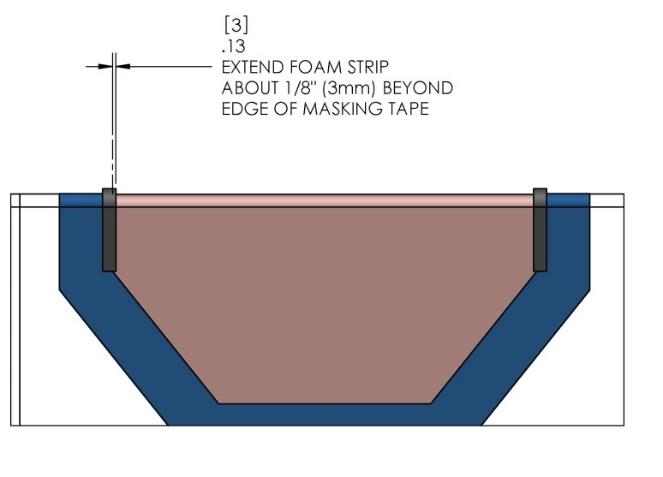
Note: If bonding saddles to a metal structure, contact Seakeeper for hull preparation instructions.
2.5.2 Bonding Saddles to Hull
Seakeeper Saddle Preparation
- Ensure that screws fastening saddles to the installation fixture are tight.
- Check that each saddle contains 4 plastic screws which will ensure an adhesive gap of 0.080 in. (2 mm) on top surface of hull as shown in Figure 15. Do not remove these screws.
- Thoroughly clean with alcohol or acetone the inside surfaces of Seakeeper foundation saddles to remove any contaminates as shown in Figure 15. Use new paper towels for cleaning, not shop rags.
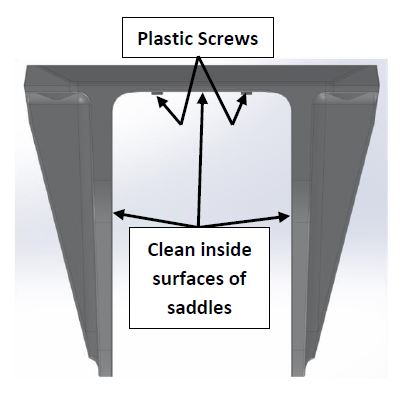
- Thoroughly sand all saddle inside surfaces with 80 grit sandpaper. (IMPORTANT – BOND STRENGTH MAY BE REDUCED IF THIS STEP IS SKIPPED.)
- Wipe surfaces clean from dust with alcohol or acetone using new paper towels, not shop rags.
- If using Plexus MA590 adhesive, apply Plexus PC-120 surface conditioner to inside surfaces of Seakeeper foundation saddles in accordance with manufacturer instructions. These instructions are located at the end of this section. If using an alternate adhesive, check with manufacturer if any surface conditioner/etch is required for the aluminum saddles.
Bonding Saddles to the Hull
Note: This is a sample if using Plexus, if using another adhesive follow manufacturer’s recommendations.
If using Plexus MA590 adhesive, the Seakeeper saddles should be installed when PC-120 is confirmed dry.
- Assemble adhesive cartridge into either the manual or pneumatic gun as shown. Remove cap on cartridge and attach mixing tip. For pneumatic gun, start with low air pressure and increase until desired flow rate is achieved.
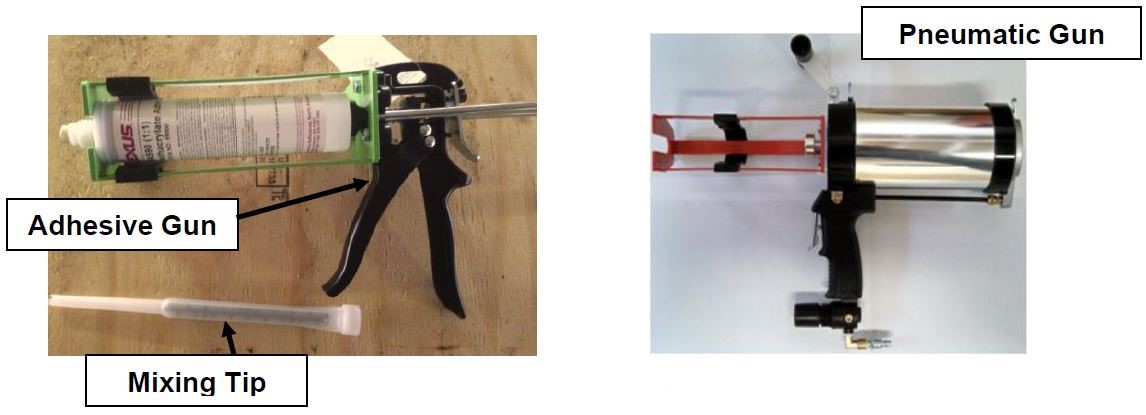

- Cut tip of mixing wand as shown in photo below.

- Prepare a second mixing wand as shown in photo below by attaching the simple flexible nozzle to the end of the mixing tip. Set aside for now as this will be used to inject adhesive into the sides of each saddle after the fixture / saddles are in position.

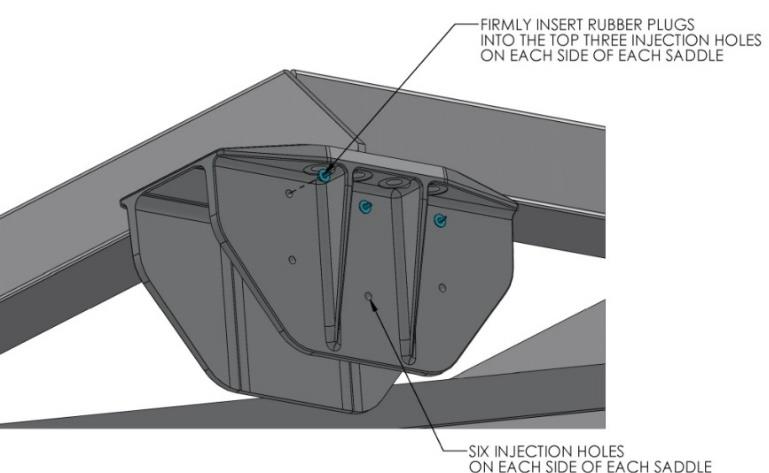
- Install provided rubber plugs in 12 holes of each saddle. The plugs will limit the adhesive being forced out of the injection holes in step 6 below.
- Apply large bead of adhesive to the hull structure as shown in the figure below. Apply approximately 1½ cartridges at each of the four locations. Work deliberate and fast as it takes some time to apply the adhesive to the structure. These working times can be reduced at elevated temperatures. Two workers should apply the adhesive at the same time to finish the installation before the adhesive starts to cure.
See TB-90382 – Structural Adhesive Recommendation for more details.
- MA590 has a working time of 90 minutes.
- SciGrip SG300-40 has a working time of 35 to 45 minutes.
- Pro-Set ADV-176/ADV-276 has a working time of 90 minutes
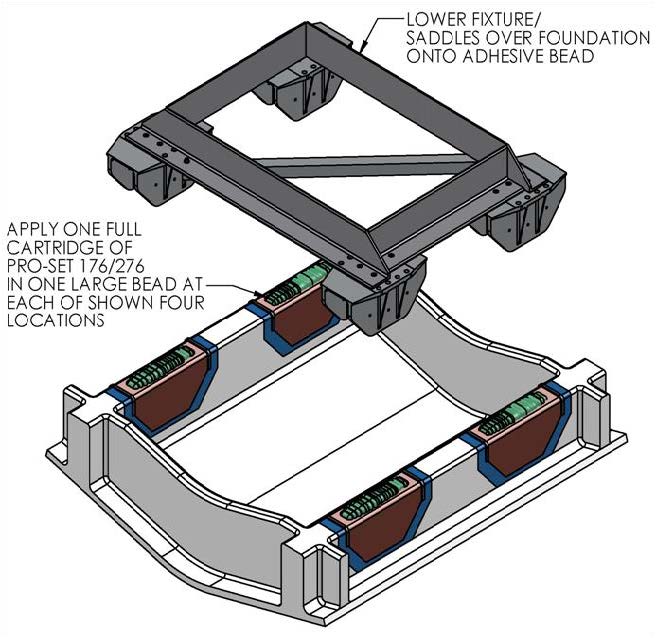
- Lower fixture and saddles over the hull structure and apply light downward pressure to each of the four saddles until the four nylon screws rest on the hull structure. The adhesive will be forced towards the forward and aft ends of each saddle and partially down the sides of the foundation beams.
- Insert full adhesive cartridge along with mixing wand / nozzle assembled in Step 3 above, into gun.
- Begin to inject adhesive into the six holes provided on each side of each of the four saddles. Follow the numbered sequence shown until the adhesive pushes out the edges of the saddle perimeter. The intent is to pump in the adhesive working from the top down and from the middle to the ends to fill the gaps and displace any air. A complete bond is required – excess adhesive will be needed to make sure all bond gaps are filled.
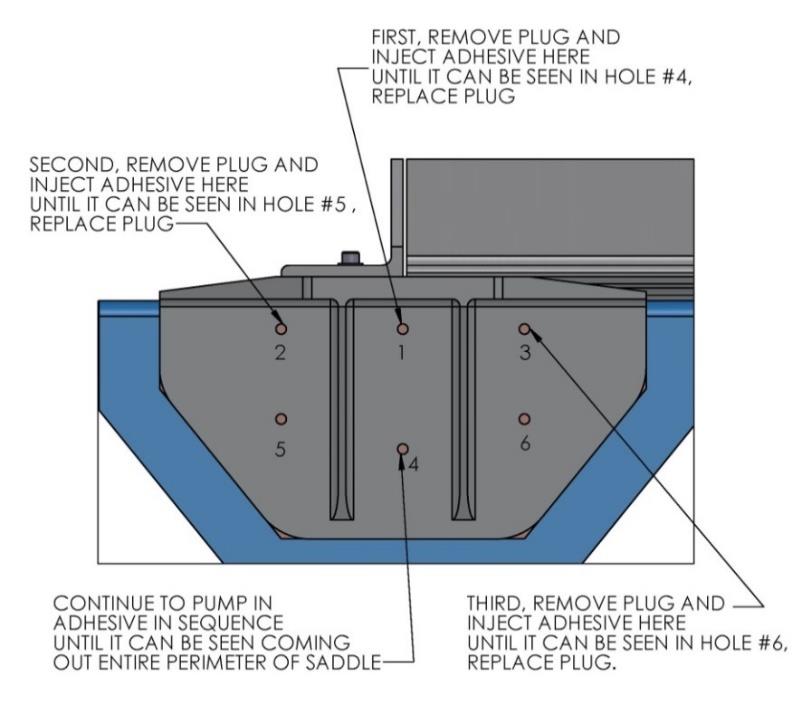
- Repeat above step for remaining 7 sides of the saddles.
- When gaps have been completely filled, clean off excess adhesive, remove foam tape, remove plugs, and remove masking tape.
- Allow adhesive to cure per manufacturer’s recommendations. Follow adhesive guidelines for curing time versus temperature prior to removing the fixture.
- Bonding of Seakeeper saddles onto the hull is now complete. Remove installation fixture.
2.5.3 Installation of Seakeeper
- Rig Seakeeper for lifting and lower it into position onto top surface of four saddles.
- Apply a small bead (approximately 4 mm wide) of sealant or caulk to the mating surfaces between the saddles and the Seakeeper foundation. Adjust position of the Seakeeper until alignment is achieved for the 32 fasteners that will attach the foundation frame to saddles. (Note: isolation gasket used for bolt-in installation is not required).
- Install Seakeeper supplied M16 fasteners as shown in figure below – apply a moderate coat of nickel based anti-seize compound to the threads of each bolt prior to installation and a small amount of marine sealant (Sili-Thane 803 or similar) to the washer faces.
- Torque all fasteners to 100 ft-lbs (136 N-m).
- Proceed to electrical and cooling portion of the installation.
3.0 Electrical Installation
3.1 Electrical Installation Introduction
This section for electrical installation explains how to mount the electrical equipment and how to connect the electrical cables (Figure 16).
Reference Documents & Drawings:
- 90710– Seakeeper 40 Cable Block Diagram
- 90716 – Seakeeper 40 Operation Manual
- 90438 – 5″ Operator Display Envelope and Mounting Details
- 90467 – Seakeeper 5″ Display Kit
- TB-90191 – Seawater Cooling Pump Recommendations
- Seakeeper Compatibility Technical Bulletins




Pump Out, 16.4 ft (5 m)
Figure 16– Electrical Equipment for Seakeeper 40
3.2 Electrical Equipment Power Connections
230 VAC Power Source Requirements
- 230 VAC (nominal), 1 Phase, 50/60 Hz, 30 A
- With installations of more than one Seakeeper, a dedicated circuit breaker should be used for each Seakeeper Motor Drive Box.
Drive Box AC Power Input Connection Instructions
- AC Power Input Cable: 3 x 10 AWG (3 x 6 mm2 CSA), 10 ft (3 m) length, (P/N 20542) Seakeeper-supplied and pre-installed in Motor Drive Box.
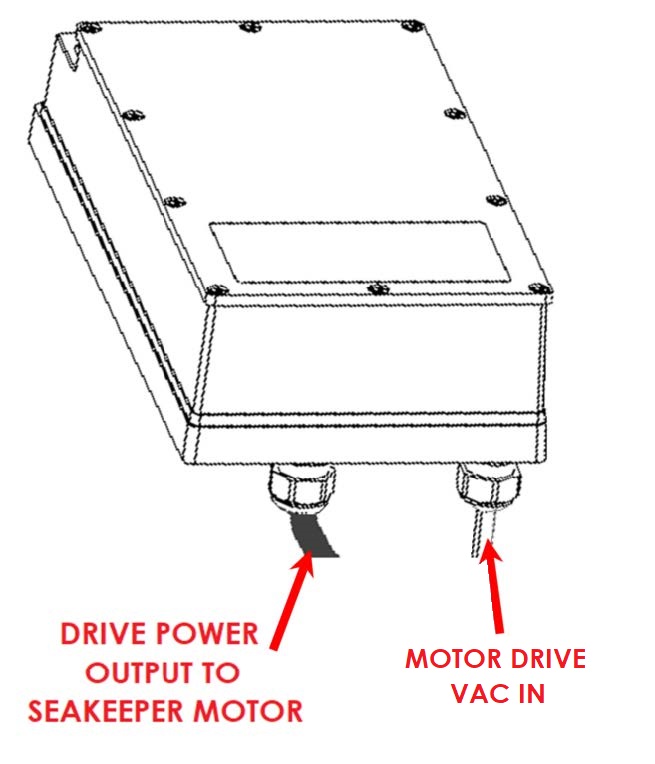
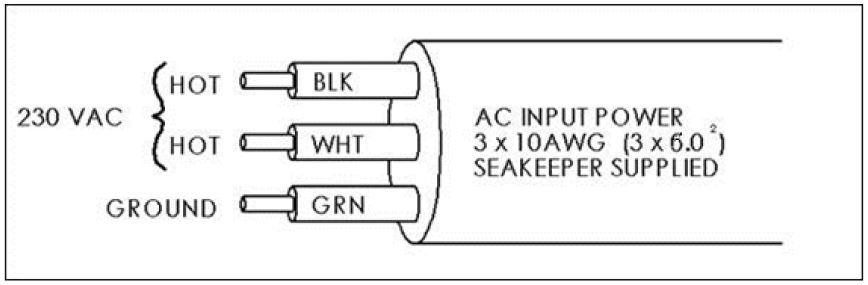
- For Seakeeper 40, connect 230 VAC wires in AC Input Cable to a 30 A, double-pole Circuit Breaker at an AC power distribution panel according to Figure 18 above.
24 VDC Power Input
- One 24 VDC, 15 A (Customer supplied breaker) for Seakeeper Control Power, AND
- One 24 VDC, 20 A (Customer supplied breaker) for DC Seawater Pump.
- A dedicated breaker breaker should be used for each Seakeeper control power and DC Seawater Pump source.
DC Power Connection Instructions

Reversing polarity on the DC power input to the Seakeeper can result in damaging the electronics in the control system.
- 24 VDC, 2 x 12 AWG (3 x 4 mm2 CSA) Seakeeper supplied.
- Install Seakeeper provided DC Power Input Cable (P/N 20248),
as shown in Drawing No. 90710 – Seakeeper 40 Cable Block Diagram.
- Route DC Power Input Cable to DC Power Distribution Panel.
- Terminate positive (B+, Red) conductor through dedicated over-current protection device (customer supplied) and a dedicated Seakeeper isolation switch (customer supplied) then directly to battery plus terminal.
- Terminate negative (B-, Black) conductor directly to battery negative terminal or negative bus.
- Before connecting DC Input Cable to Seakeeper, check for proper voltage and polarity with a DC multimeter using Figure 19 below.
- Connect DC Input Cable to 24 VDC input receptacle on Seakeeper.
- Install Seakeeper provided DC Power Input Cable (P/N 20248),
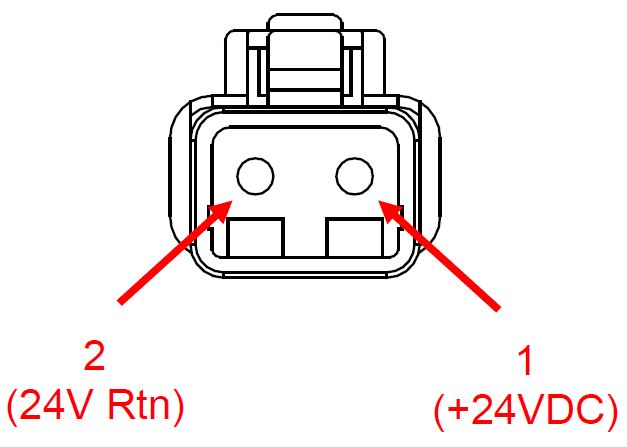

When energizing DC power for the first time, if ConnectBox does not power up immediately then disconnect and inspect connector polarity.
DC Seawater Pump 24 VDC Power Input Connection Instructions

Connecting the DC Seawater Pump in any other manner than recommended by Seakeeper may cause internal failure.
- Install Seawater Pump Input Cable (P/N 20248) to overcurrent protection corresponding to Seawater Pump selected as follows:
- Connect the 12 AWG positive conductor (Red) through dedicated overcurrent protection device (Customer supplied), maximum of 20 A, to dedicated battery isolation switch.
- Connect 12 AWG negative conductor (Black) directly to battery negative terminal or DC main negative bus bar.
- Before connecting Seawater Pump Input Cable to Seakeeper, check for proper voltage and polarity with a DC multimeter using Figure 20 below.
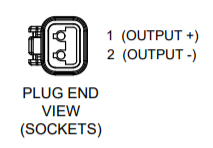
- Connect Seawater Pump Input Cable to “SW Pump 24 VDC In” connector on the Seakeeper.
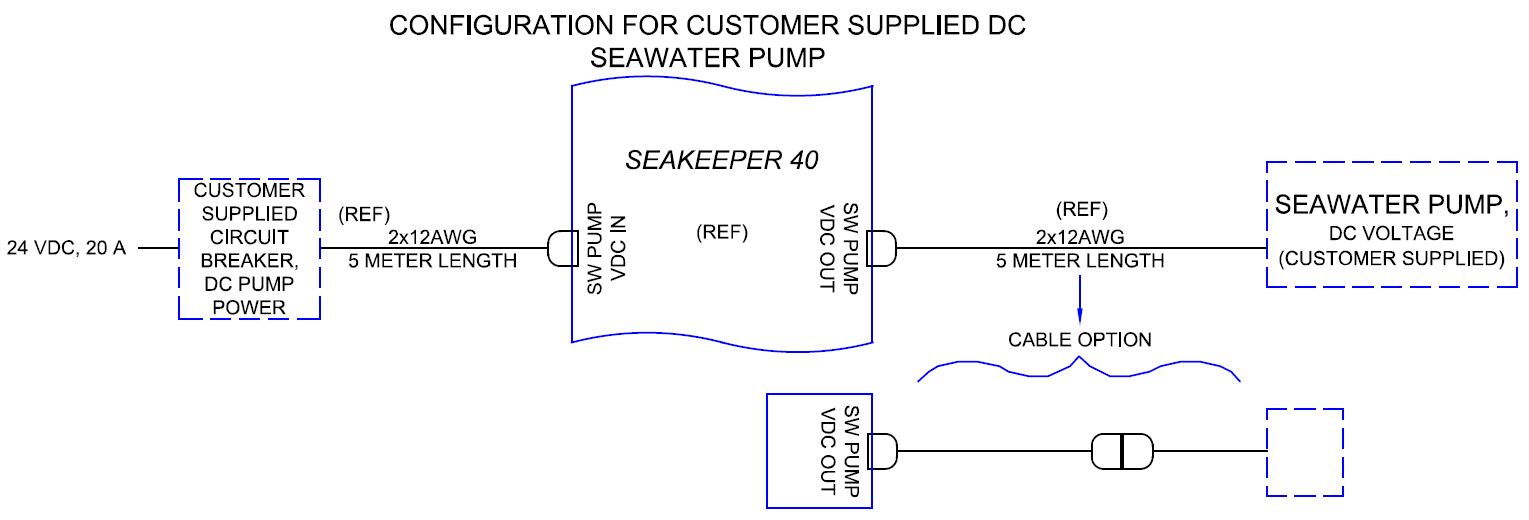
DC Seawater Pump 24 VDC Power Output Connection Instructions
- Connect Seawater Pump Output Cable (P/N 20594) to the Seakeeper 40 “SW Pump 24 VDC Out” for DC power output to the Seawater Pump.
- Seawater Pump Output Cable is a 2 x 12 AWG cable, 16 ft (5 m) length, with a size 12 female Deutsch plug.
- Cable P/N 20594 has two ring terminals for connection to DC Seawater Pump P/N 30529. A cable option exists for attaching a Deutsch connector (as shown below). See Drawing 90710 – Seakeeper 40 Cable Block Diagram notes for details.
- Customer-supplied pumps rated at 24 VDC, 20 A maximum, customer supplied, must be configured with a Deutsch DTP-04 series, 2-pin male receptacle (Figure 21) to mate with the Seawater Pump Output Cable female connector.

(DTP04-2P)
- Seawater Pump Output Cable must be routed and installed in the vessel from the Seakeeper 40 “SW Pump 24 VDC Out” Deutsch connector to the DC Seawater Pump cable. See Figure 22 for details.
3.3 Electrical Equipment Ground Connections
Seakeeper to Vessel Ground Connection Instructions
- Connect the Seakeeper foundation to vessel ground.
- Install Ground Cable (10 AWG or 6.0 mm2, Customer supplied) from the M6 brass ground stud on the Seakeeper rear foundation (Figure 23) to a suitable vessel ground. The ground cable should be installed on the inside rear of the foundation as shown below. If possible, install ground cable prior to installing the Seakeeper into the vessel. If there is no access to the ground stud from below the rear of the Seakeeper once installed, the rear cover, upper rear cover, and GCM bracket will need to be removed to access the ground stud from above the Seakeeper.

NOTE: USE ONLY THIS LOCATION FOR GROUNDING THE SEAKEEPER TO THE VESSEL GROUND.
2. Install Ground Cable (10 AWG or 6.0 mm2, Customer-supplied) from the M6 brass ground stud on the
Seakeeper rear brace to a suitable vessel ground.
- EN/IEC 90204-1 Clauses 6.3.3 and 8.2.3
- ABYC E-11 July 2018 Clauses 11.5.2 and 11.16.1.
3. Ground connection should be made with vessel bonding system, if available. However, the ground is not
referring specifically to a bonding system but for outboard boats generally refers to the outboard engine
negative terminal. Per ABYC E-11 (2018), Clause 11.5.2.7.4: If the negative side of the DC system is to be
connected to the ground, the connection shall be made only from the engine negative terminal, or its bus,
to the DC grounding bus. This connection shall be used only as a means of maintaining the negative side of
the circuit at ground potential and is not to carry current under normal operating conditions.
4. A proper ground connection is critically important for corrosion protection and helps to ensure the
ignition protection of the unit by ensuring it does not carry any stray current.
ABYC E-11, figure 4A
3.4 ConnectBox Display Connections
A display is required with the installation of a Seakeeper 40 to support the full functionality of the unit through the Seakeeper App in addition to the ConnectBox. The Seakeeper App provides an interface for controlling the Seakeeper or viewing the Settings, Service, Info, and Alarm pages. The Seakeeper ConnectBox can be helm-mounted to provide an additional interface for the control of the Seakeeper but does not replace the need for a Seakeeper compatible display.
The Seakeeper 40 has several options for establishing a Seakeeper display interface to support the Seakeeper App:
- Preferably, connect the Seakeeper to a compatible Multifunction Display (MFD).
- Install an optional Seakeeper 5″ Touch Display (P/N 90467).
- A combination of a compatible MFD and an optional 5″ Touch Display is also available.
The following figure provides a schematic of the preferred display option. The subsequent sections outline the instructions and references for connecting the Seakeeper 40 in each of these display options.
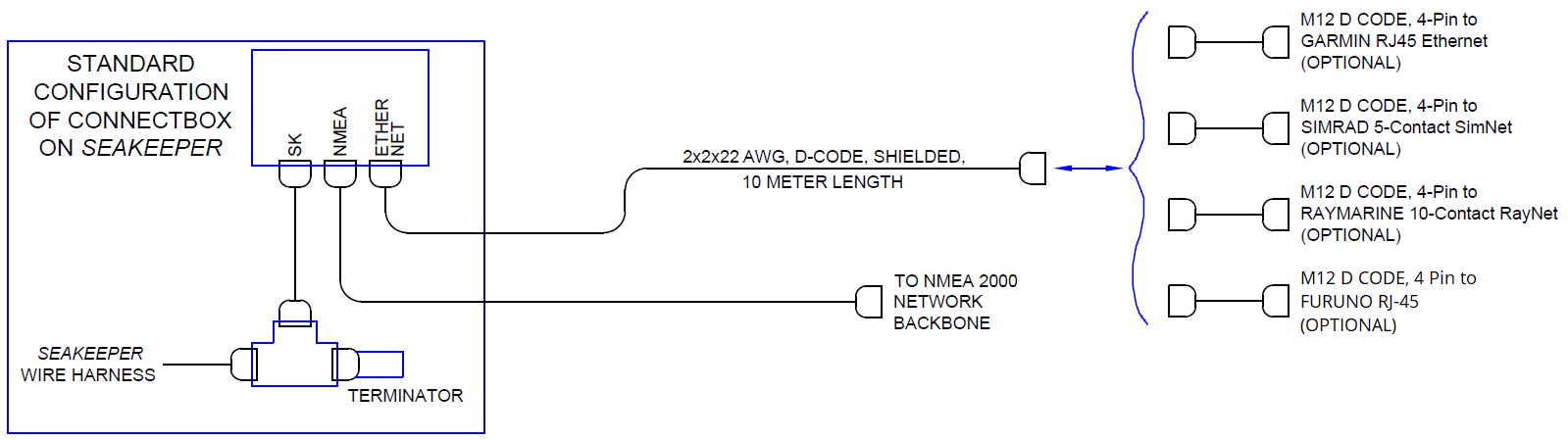
Reference Documents & Drawings
Connecting to a Compatible MFD
- The Seakeeper 40 can be connected to a variety of available MFD systems. Refer to the Technical Bulletins Section of the Seakeeper Technical Library for manufacturer specific MFD compatibility technical bulletins.
- MFD specific Technical Bulletins will be updated regularly as new MFD systems become compatible. Currently GARMIN, RAYMARINE, NAVICO (Simrad, Lowrance, B&G), and FURUNO offer compatible MFD models.
- Once a compatible MFD has been selected, refer to the appropriate manufacturer specific compatibility Technical Bulletin listed above for integration instructions.
- Connect Seakeeper-supplied M12 D-Code, 82 ft (25 m), cable (P/N 30355) to MFD manufacturer-specific Ethernet adapter cable. Custom Ethernet cables for specific MFD manufacturers are available through Seakeeper and must be purchased with the Seakeeper 40 when connecting to an MFD.
Connecting to an Optional Seakeeper 5″ Touch Display
If not utilizing a compatible MFD display, a Seakeeper 5” Touch Display must be purchased from Seakeeper. The Seakeeper 5” Touch Display (P/N 90467) includes the components shown in the following figure and will be integrated with the ConnectBox.
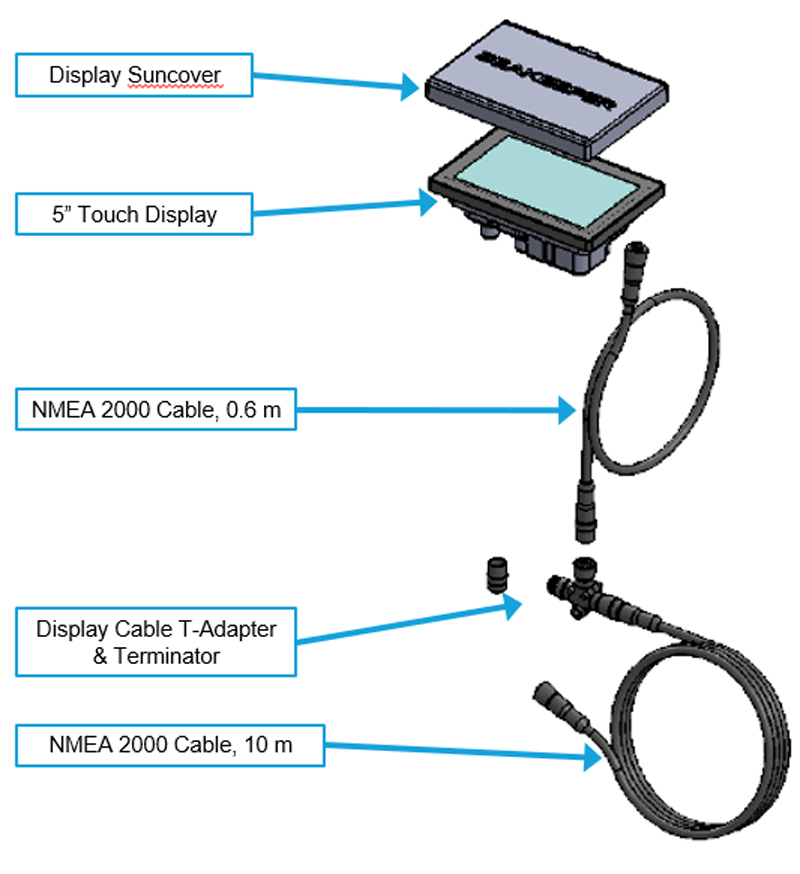
P/N 90467 (P/N 30300, 6 ft (1.8 m) USB Extension
Cable not shown)
- Determine location of Seakeeper 5” Touch Display:
- The desired location of the 5” Touch Display must be determined with respect to the vessel’s arrangement.
- The 5” Touch Display should be located on or near the helm or another easily accessible location.
- Route CAN communications cable:
- The CAN Cable, (labelled NMEA 2000 Cable in figure above), is a 32 ft (10 m) shielded cable that connects the ConnectBox Tee adapter to the 5” Touch Display.
- NOTE: Cable lengths are also available in 25, 35, 50, and 65 meters
- The NMEA 2000 cable must be routed and installed in the vessel from the Seakeeper 40 wire harness CAN Tee to the Tee Adapter at the Seakeeper 5” Touch Display, included with P/N 90467.
- The CAN Cable, (labelled NMEA 2000 Cable in figure above), is a 32 ft (10 m) shielded cable that connects the ConnectBox Tee adapter to the 5” Touch Display.
- Install Seakeeper 5″ Touch Display equipment:
- Console space required: Approx. 5.24 W x 3.70 H in. (133 x 94 mm)
- Mounting Instructions, Surface Mount: see Envelope and Mounting Details, in Drawing No. 90438 – 5” Display Envelope and Mounting Details.
- CAN communications tee adapter and terminator mounting instructions:
- Console space required, Rear: Approx. 4 W x 3 H in. (102 x 76 mm)
- Mounting Instructions: Rear mount on vessel console panel, within 2 ft (0.6 m) of Display.
- Hardware required: One mounting screw for 0.197 in. (5 mm) diameter mounting hole on Tee Adapter.
- Connect Seakeeper 5” Touch Display Equipment:
- The Seakeeper 5” Touch Display is connected in accordance with figure below.
- The USB Extension Cable is 6.5 ft (2 m) long cable that enables software updating on a 5″ Touch Display where accessibility to rear panel is limited.
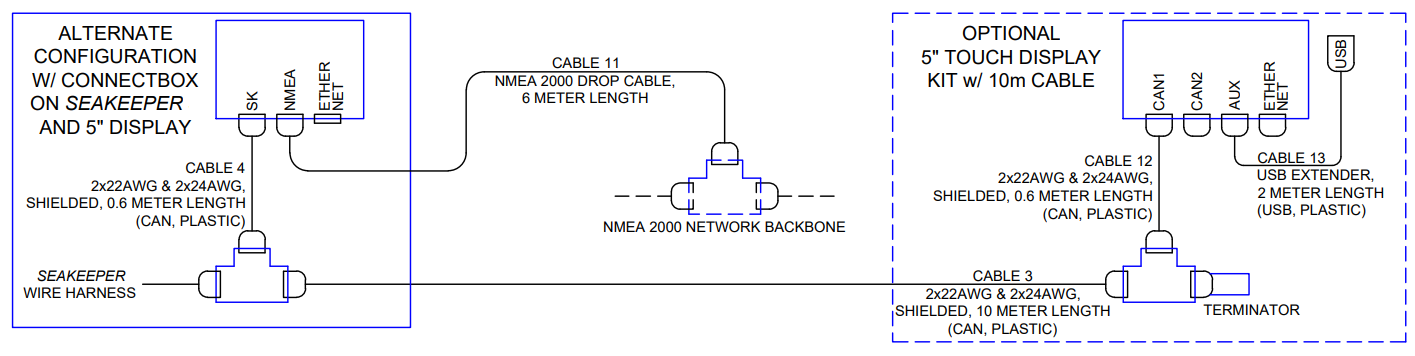
NMEA 2000 Network Connection
The Seakeeper 40 requires a connection to the vessel’s NMEA 2000 network backbone via a drop cable for access to the GPS signal. The Seakeeper 40 will monitor information on the NMEA network to support and optimize the performance of the Seakeeper 40. If no GPS signal is detected, a warning will appear on the Seakeeper display. The Seakeeper will not spool-down, but the operation of the unit will be limited until the GPS signal returns.
- Install customer-supplied NMEA 2000 Tee Adapter (space required: approximately 4 W X 3 H in. (102 X 76 mm).
- Connect NMEA Backbone to Tee Adapter.
NOTE: NMEA drop cable can be no longer than 19.6 ft (6 m) in length. - Connect Seakeeper-supplied NMEA cable (P/N: 30332) to the customer-supplied NMEA 2000 Tee Adapter on vessel’s NMEA 2000 backbone.
- An active NMEA 2000 compatible GPS signal is required on the vessel’s NMEA 2000 backbone to operate the Seakeeper 40.
- If no GPS signal is detected, a Speed Over Ground (SOG signal) warning will be present on the Seakeeper app. See TB-90640 for NMEA connectivity guidance.
- An active NMEA 2000 compatible GPS signal is required on the vessel’s NMEA 2000 backbone to operate the Seakeeper 40.
ConnectBox Helm Mounting – Optional
- Console space required: Approx. 3.41 L x 4.15 W in. (87 x 106 mm).
- Mounting Instructions, Surface Mount: See Drawing No. 90558 – Seakeeper ConnectBox Helm Mounting Kit, for details. Seakeeper ConnectBox 3D Model available upon request.
- Mount ConnectBox Replacement Blank insert into Seakeeper 40 top cover at the original location of the ConnectBox.
4.0 Cooling Installation
4.1 Cooling Installation Introduction
The Seakeeper 40 is shipped with the cooling circuit filled and ready for use. Only a quick confirmation of glycol level is required.
Reference Documents
- 90710 – Seakeeper 40 Cable Block Diagram
- 90711 – Seakeeper 40 Cooling Water Schematic
- 30529 – 24 VDC Seawater Pump Assembly
- TB-90191 – Seawater Cooling Pump Recommendations
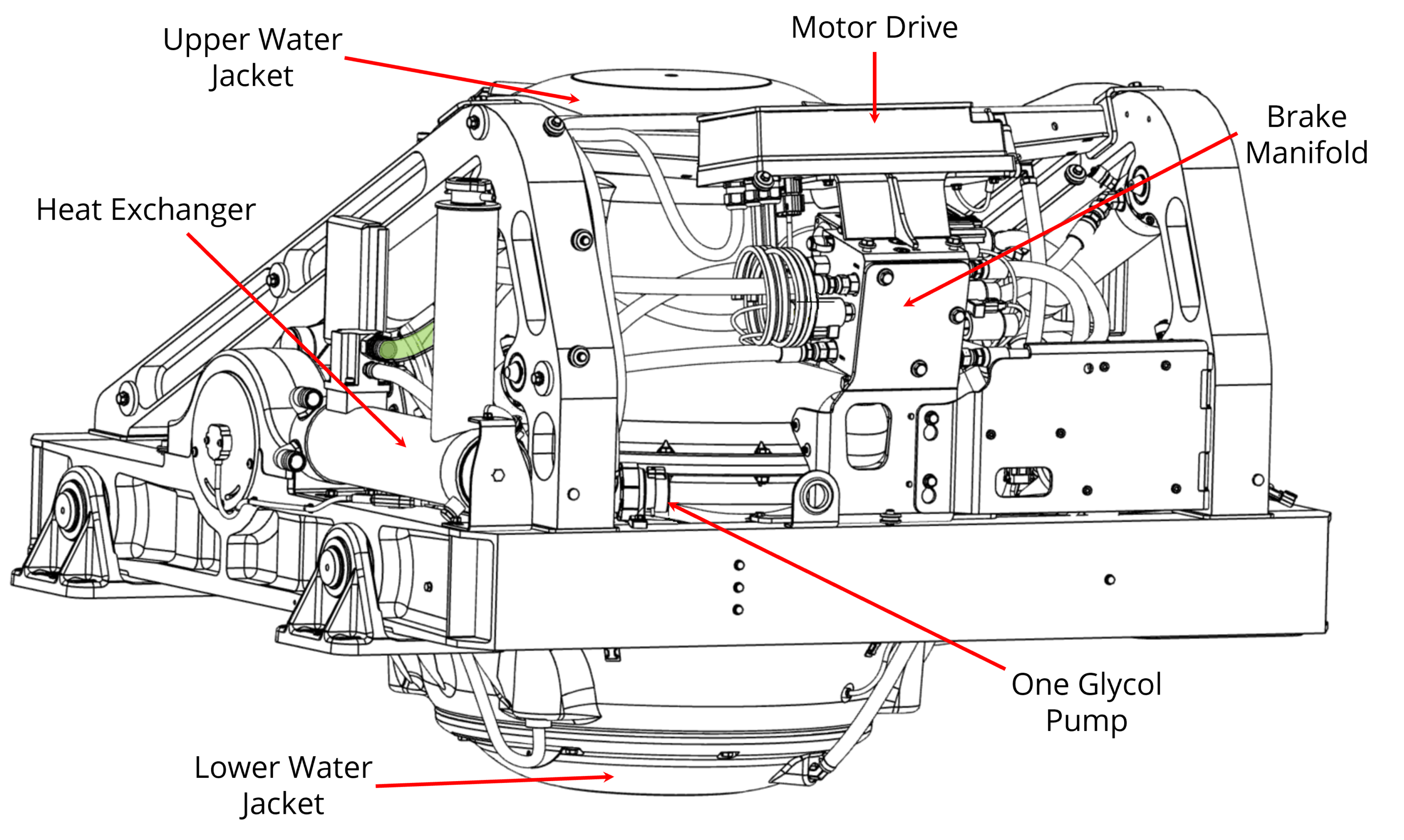
4.2 Installation Considerations
- Installer is responsible for supplying a dedicated seawater pump and associated plumbing. Seawater connections on the heat exchanger mate with 1 in. (25.4 mm) hose. An optional seawater pump can be purchased through Seakeeper (P/N 30490).
- There is no need to disconnect hose from glycol pump except to replace the pump. In this case, provision will need to be made to catch draining glycol as plumbing is disconnected. Use caution to avoid breaking plastic hose connections on pump casing.
- An output is available from the Seakeeper 40 wire harness to power and automatically control seawater pump. This pump must operate on 24 VDC and consume less than 20 A. Pumps requiring other voltages or higher current can still be controlled by using this supply from the wire harness to trigger an installer-supplied contactor, but a separate source of power must be provided.
- The seawater pump is powered by Seawater Pump Output Cable, via “SW Pump 24 VDC Out” on the Seakeeper 40, as outlined in Electrical Installation section.
- A dedicated through-hull fitting should be installed for each Seakeeper unit onboard the vessel to ensure sufficient seawater flow to each unit.
- It is recommended the seawater pump be installed below the waterline, as close to baseline of the vessel as practically possible, to maintain positive inlet pressure on the pump in all operating conditions.
- A self-priming seawater pump may be required to maintain water flow in all underway conditions. Cavitation can occur at the seawater inlet and potentially cause an air-lock condition restricting seawater flow to the heat exchanger.
- Maximum seawater pressure in heat exchanger is 20 psi (1.4 bar).
- Seawater flow requirement through heat exchanger is 13 GPM (49 LPM) minimum and 15 GPM (57 LPM) maximum under all operating conditions of the boat. When sizing seawater pump, installer should factor in losses for raw water plumbing. In addition to initial operation at dock, new Seakeeper installations should be checked to be within the flow requirements while vessel is at speed. Flows higher than 15 GPM (57 LPM) could affect heat exchanger life.
- Vented loops (shown in Figure 27) are optional and should only be considered with centrifugal style pumps. Self-priming or positive displacement style pumps do not require a vented loop, including Seakeeper supplied optional pump (P/N 30490).
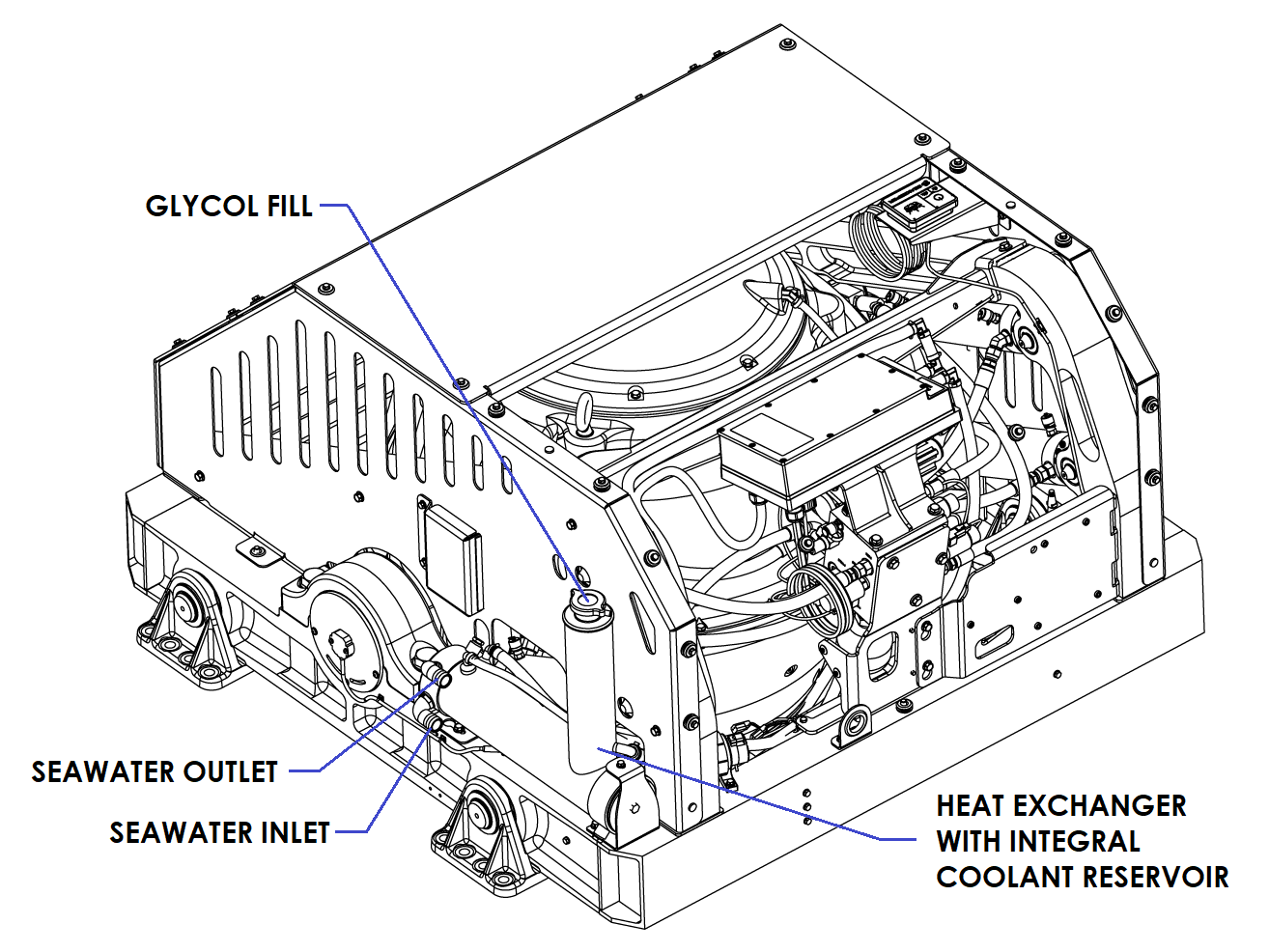
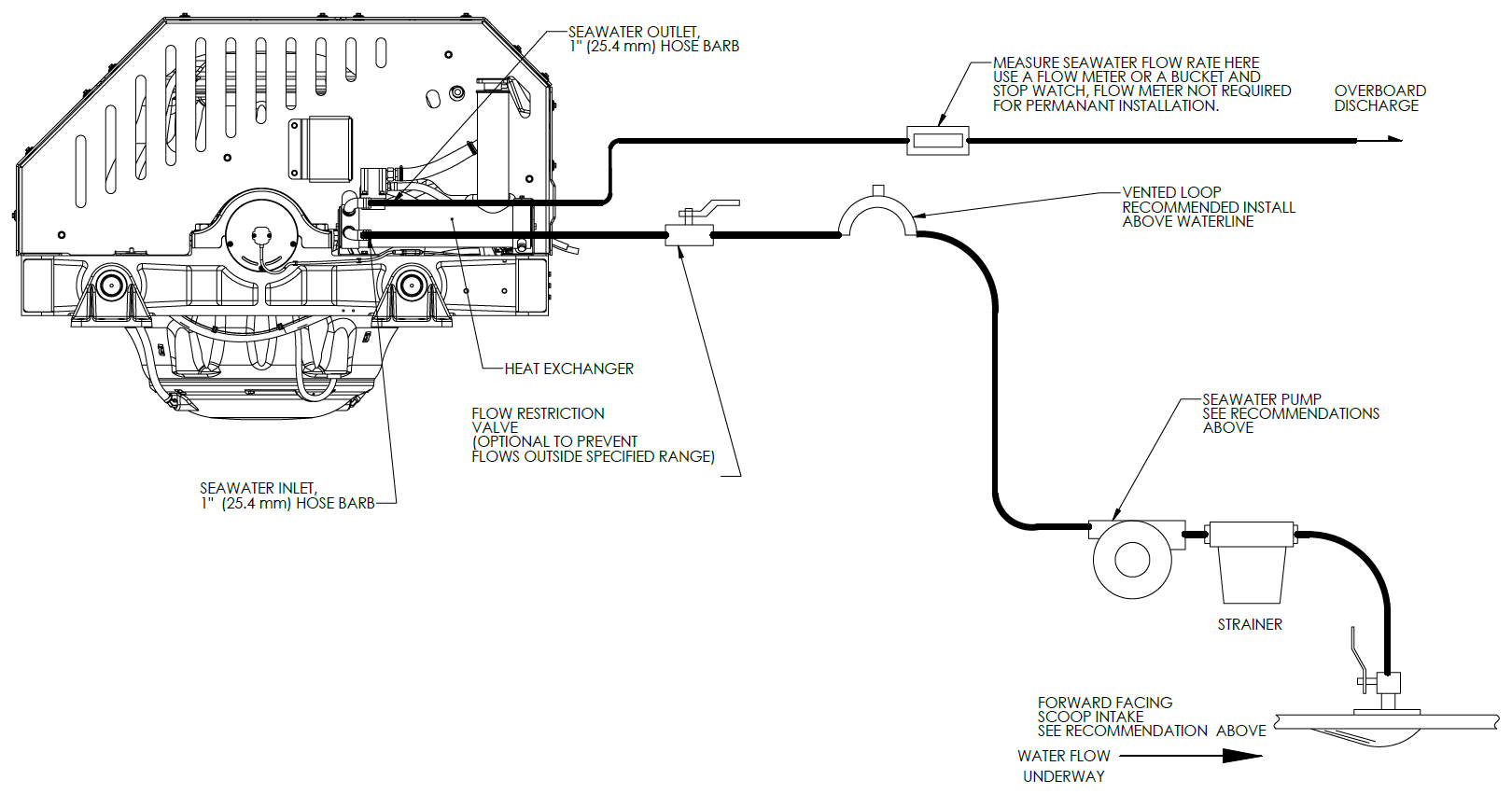
4.3 Connecting Seawater to Heat Exchanger
Connecting Seawater Pump to Heat Exchanger
- Connect seawater from installer-supplied pump to lower 1 in. (25.4 mm) hose barb on heat exchanger. Use the same practices as other below waterline seawater plumbing. Required flow rate is 13 GPM (49 LPM) minimum and 15 GPM (57 LPM) maximum.
- Connect seawater discharge (upper hose barb) to overboard drain. Use the same practices as typical below waterline seawater plumbing.
- In addition to initial operation at dock, new installations should be checked with a flow meter for minimum 13 GPM (49 LPM) and maximum of 15 GPM (57 LPM) flow under all normal operating conditions.
- If no other method of confirming flow is available, discharge line may be temporarily diverted to a bucket. Flow is calculated from time to fill a known volume.
- A self-priming seawater pump (customer/installer supplied) may be required due to installation location to maintain water flow in all underway conditions where cavitation near the intake may occur and potentially cause an air-lock condition restricting seawater flow to the heat exchanger.
- Inspect raw water plumbing after sea trial for any signs of leakage.
- Heat exchanger contains removable end-caps to provide access for cleaning the tube bundle.

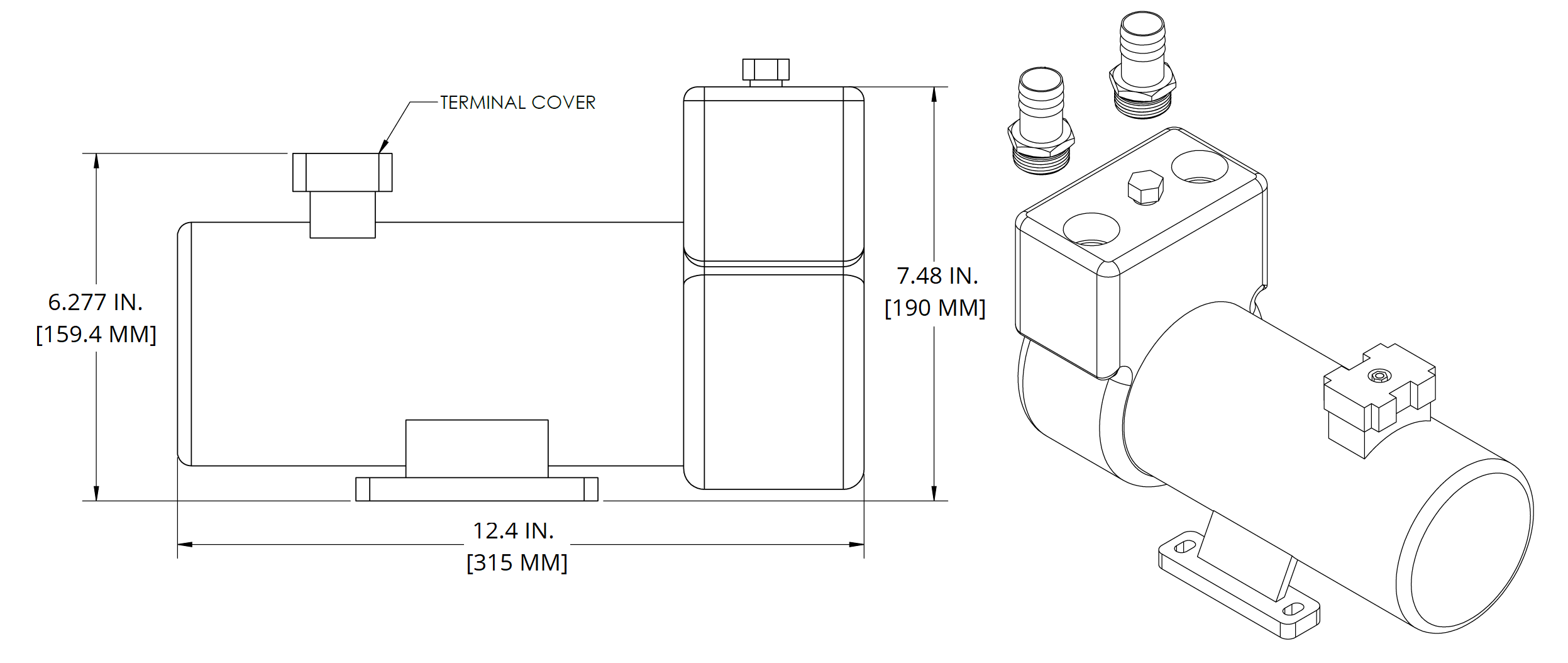
Seakeeper Optional DC Seawater Pump (P/N 30529)
- Seakeeper offers a self-priming DC Seawater Pump as an optional addition, P/N 30529 – 24 VDC Seawater Pump, shown in Figure 29.
- Pump fittings are 3/4 in. NPT. To connect to Seakeeper 40 heat exchanger, a 3/4 to 1 in. barbed adapter will be necessary. DO NOT use bronze or brass fittings on the optional DC Seawater Pump. Use pipe sealant on the threads and other connections.
- The base does not require direct mounting if one of the pipe flanges is rigid mounted. Do not rigid mount both the flanges and the base to avoid mounting tolerances that may distort the motor base. Install the pump with the shaft in a horizontal direction. NEVER install the pump vertical with the motor below the pump.
- Figure 29 provides a mounting hole dimensions for mounting the DC Seawater Pump.
- The pump assembly is pre-wired for connection to the Seakeeper 40 wire harness through Cable 5. The pump specifications are as follows:
| Voltage | 24 VDC |
| Overcurrent Protection Rating | 20 A |
| Suction Lift | 26 FT |
| Flow Rate | 23 GPM with 10 FT suction head |
| Ignition Protection | ISO 8846 or equivalent |
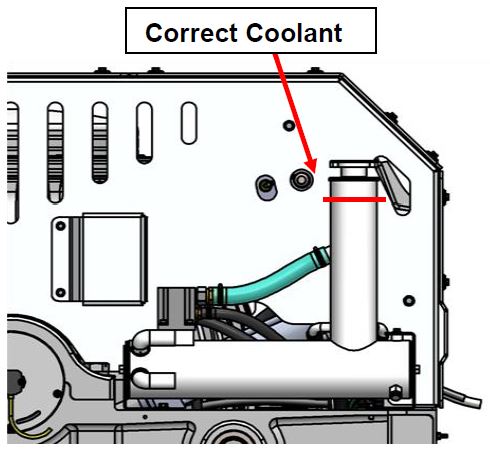
4.4 Adding Coolant
- Cooling system is filled to proper level when shipped, with a mixture of 50% ethylene glycol and 50% distilled water. The clear tube between the thermostat housing and reservoir should be filled with green coolant mixture. If level has dropped, check for evidence of leaks at all connections before adding fluid as described below. If coolant is at the correct level, skip to Section: Connecting Seawater to Heat Exchanger.
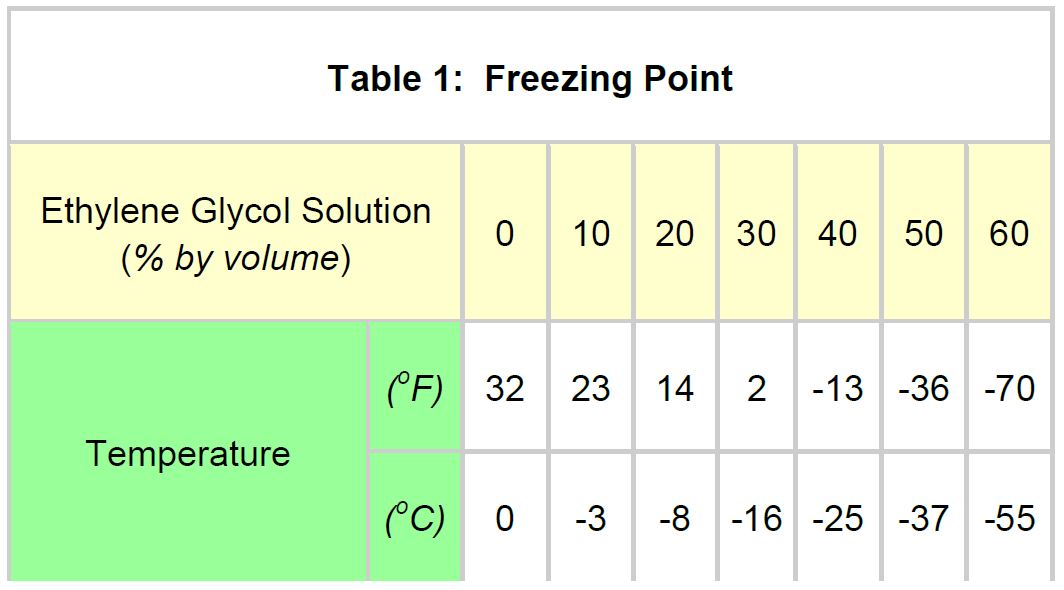
- Mix 50% ethylene glycol with 50% distilled water in a clean container. Refer to Table 1 or glycol manufacturer’s literature for freezing points.
- Remove pressure cap on top of reservoir. Pour mixture in until level is 1 – 2 inches from top of reservoir as shown in Figure 30. Filling reservoir above this level will not cause any damage but coolant may be expelled from pressure relief port below cap due to normal thermal expansion of coolant.
- Connect 24 V to controller.
- At the Display check for any ALARMS

- Press the POWER ON/OFF button.

- The flywheel will start to spin and the glycol pump will start.
- Recheck glycol level with fluid circulating in coolant circuit. Sight down inside reservoir and check that coolant level is above upper port on reservoir as shown in Figure 30. Replace cap.
- After several minutes of running, press POWER ON/OFF button
 to turn power off to the flywheel and glycol pump.
to turn power off to the flywheel and glycol pump.
- At the Display check for any ALARMS
- The cooling system is self-purging. If small amounts of air are in the system, they will most likely be dislodged during the first sea trial. Re-check level after sea trial and add fluid if required.
5.0 Installation Requirements
5.1 Installation Requirements Introduction
The Installation Requirements section outlines the components and tools needed for the Seakeeper 40 Installation that are not included within the scope of supply.
5.2 Required Supplies for Seakeeper Installation
Required Supplies Needed for Seakeeper Installation
(Not Supplied With the Seakeeper)
| Item | Description | Qty | Installation Manual Reference Section | Other Reference | System |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Adhesive and cleaning supplies (for bond-in installation) (Total area of adhesive is 1,300 in.2 (8,387 cm2)) | AR | 2.5 Mechanical Installation | Adhesive manufacturer’s instructions and Dwg 90878 | Mechanical |
| 2 | Soundproofing Considerations | AR | 2.2 Selection of Installation Location | Mechanical | |
| 3 | Spreader bar for lifting Seakeeper | 1 | 1.2 Transport and Unpacking | P/N 80029 | Mechanical |
| 4 | Hose clamps for seawater plumbing to 1 in. (25.4 mm) hose barb (2 per hose barb) | 4 | 4.3 Connecting Seawater to Heat Exchanger | Cooling | |
| 5 | 3/4″ to 1″ Hose Adapter | 1 | 4.3 Connecting Seawater to Heat Exchanger | Cooling | |
| 6 | Circuit Breaker, AC, 2-Pole, 20 A | 1 | 3.2 Electrical Equipment Power Connections | Dwg 90710 | Electrical |
| 7 | Circuit Breaker, DC, 1-Pole, 15 A for control power | 1 | 3.2 Electrical Equipment Power Connections | Dwg 90710 | Electrical |
| 8 | Circuit Breaker, DC, 1-Pole, 20 A for seawater pump | 1 | 3.2 Electrical Equipment Power Connections | Dwg 90710 | Electrical |
| 9 | M6 terminal lug for grounding Seakeeper at rear of foundation | 1 | 3.3 Electrical Equipment Ground Connections | Electrical | |
| 10 | Cable, 10 AWG, for grounding Seakeeper at rear brace to vessel ground | AR | 3.3 Electrical Equipment Ground Connections | Dwg 90710 | Electrical |
| 11 | Seawater pump, 24 VDC | 1 | 3.2 Electrical Equipment Power Connections | P/N 30490 available | Electrical |
| 12 | Relay for seawater pump control (Optional) | 1 | 3.2 Electrical Equipment Power Connections | Electrical | |
| 13 | Sili-Thane 803 Sealant (or equivalent) | AR | 2.4.3 Mechanical Installation 2.5.3 Mechanical Installation | Mechanical | |
| 14 | Nickel-based Anti-Seize | AR | 2.4.3 Mechanical Installation 2.5.3 Mechanical Installation | Mechanical |
AR = As Required
Dwg = Drawing
5.3 Tools Required for Installation
List of Common Tools That May Be Required for Installation
| Item | Description | Use |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Wire cutter | DC Power, AC Power cables |
| 2 | Wire stripper | DC Power, AC Power cables |
| 3 | Phillips head screwdriver | Cover Panels |
| 4 | 13 mm Socket Wrench | Cover Panels |
| 5 | 3 mm hex key | Gimbal sensor mount plate |
| 6 | 2.5 mm hex key | Gimbal angle sensor |
| 7 | ¼ in. nut driver/flat tip screwdriver | Hose clamps |
| 8 | Terminal or quick disconnect crimper | Power cables |
| 9 | Utility knife | Scoring cable jackets |
| 10 | 10 mm Socket Wrench | Ground stud & panels |
| 11 | Hoist, Forklift, or Crane | Unpacking and lifting Seakeeper into position |
| 12 | Drill/Drill Press | Bolt hole penetrations |
| 13 | Threaded Insert Installation Kit (Blind Hole Installation only) | Tap and install threaded inserts for M16-2.0. 1-inch length |
| 14 | 1/2 in. Drive Torque Wrench | Foundation fastener torqueing |
| 15 | 24 mm Socket, 1/2 in. drive | Foundation mounting screws |
| 16 | Fish tape | Cable pulls |
| 17 | Hole Saw | Through-hull fittings |
6.0 Installation and Start Up Checklist
6.1 Installation and Start Up Introduction
Reference Documents:
- 90437 – Seakeeper Commissioning Form
- SWI-105 – Commissioning Checklist
- Seakeeper 40 Operation Manual
The Installation and Start Up Checklists in this section provide an overview of the primary steps covered in the installation manual and should be referenced throughout the installation process. Upon completion of the
Seakeeper 40 installation, the installer should commission each Seakeeper unit with the Seakeeper Commissioning Form (90437). The Commissioning Checklist Work Instruction (SWI-105) provides a checklist of items to inspect and verify during the commissioning process and serves as a supplement to the Seakeeper Commissioning Form (90437).
All Seakeeper stabilizers should be commissioned to verify installation specifications and requirements have been implemented properly. The commissioning process should include completion of the Seakeeper
Commissioning Form (90437), all the items in the Installation Checklist, and verification of Seakeeper 40 operation without alarms or abnormal behavior.
6.2 Installation Checklist
Please Complete Checklist and E-mail to support@seakeeper.com.
Mechanical Checklist
(Reference Installation Manual Section: Mechanical Installation)
- Seakeeper foundation installed in hull
- Foundation bolts torqued to specification
Electrical Checklist
(Reference Seakeeper Drawing No. 90710 – Seakeeper 40 Cable Block Diagram & Installation Manual Section: Electrical Installation)
Mount Components
- Display (near helm)
Connect Customer Supplied Cables
- Ground Cable (Customer Supplied)
- Install lugs on both ends of customer-supplied 10 AWG ground cable
- Connect one end of Ground Cable to nearest vessel ground and other end to Seakeeper foundation frame
Connect Seakeeper Supplied Cables
- DC Input Power Cable (Seakeeper supplied)
- Connect the DC Input Power Cable from Seakeeper to 24 VDC power at customer-supplied connection box or directly to circuit breaker
- Plug connector of DC Input Power Cable into mating connector on Seakeeper wire harness
- AC Power Input Cable (Seakeeper Supplied)
- Connect the AC Power Input Cable from Drive Box to 230 VAC single phase at customer-supplied connection box or directly to circuit breaker
- CAN Communication Assembly (Seakeeper Supplied)
- Connect female end of CAN communications Cable to mating connector on Seakeeper wire harness
- Route CAN communications Cable from Seakeeper to helm (male end goes to helm)
- Connect male end of CAN communications Cable at helm to CAN Tee Adapter
- Connect Display and Seakeeper-supplied 24 in. (0.6 m) cable to CAN Tee Adapter with CAN Terminator
- Seawater Pump Power Output Cable (Seakeeper Supplied)
- Connect Seawater Pump Power Output Cable from Seakeeper wire harness to customer-supplied 24 VDC seawater pump
- Seawater Pump Power Input Cable (Seakeeper supplied)
- Connect the Seawater Pump Power Input Cable from Seakeeper DC SW Pump In to 24 VDC power at customer supplied connection box or directly to circuit breaker
Cooling Checklist
(Reference Installation Manual Section: Cooling Installation)
- Verify coolant level in heat exchanger coolant reservoir.
- Connect seawater hoses / open sea cocks to heat exchanger and test seawater pump.
- Verify 13 GPM (49 LPM) minimum and 15 GPM (57 LPM) maximum seawater flow through heat exchanger under all operating conditions of the boat.
6.3 Start Up Checklist
(Reference Installation Manual Section: Start Up & Operation Manual Section: System Operation)
- Remove lifting eyes, install sealing fasteners in lifting holes, and install cover panels
- Check polarity of 24 VDC power per Section: Electrical Equipment Power Connections – DC Power and Seawater Pump Connection Instructions.
- Turn on 24 VDC circuit breakers for control power and DC Seawater Pump
- Turn on 230 VAC circuit breaker
- Verify display works and no ALARMS are present
- If display does not work, turn off both circuit breakers immediately.
- Follow instructions in Operations Manual Section: Start Up Instructions to turn on the Seakeeper
- Verify that no ALARMS are present
- Follow instructions in Section: Start Up Instructions to turn off the Seakeeper
- AC & DC power and seawater pump may be turned off after the Seakeeper is turned off by placing the Seakeeper in LOCK mode and turning the Seakeeper off.
- Seakeeper 40 takes 4+ hours to coast down to 0 RPM from full speed
7.0 Revision History
| Revision | Description | Date |
| 1 | Initial release | 09SEP2023 |
| 2 | Added ConnectBox and Bond-in installation instructions | XXJAN2024 |